Q1. If A, B, C are interior angles of  ABC, show that:
cosec2
ABC, show that:
cosec2 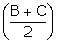 - tan2
- tan2
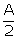 = 1
= 1
Solution
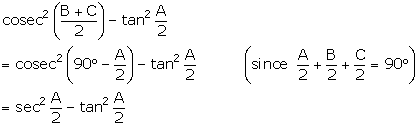 = 1 (since, sec2
= 1 (since, sec2
Q2. If acos θ + bsin θ = 4 and asin θ - bcos θ = 3, then a2 + b2 is
Solution

Q3. If  , then
, then 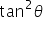 equals to:
equals to:
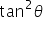 equals to:
equals to:Solution
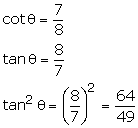
Q4. If 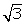 tan
tan 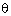 = 3 sin
= 3 sin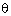 , find the value of sin2
, find the value of sin2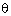 - cos2
- cos2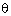
Solution
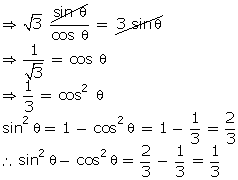
Q5. The express sin A in terms of cot A is:
Solution
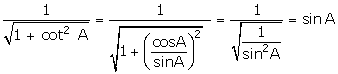
Q6. Prove
that (cosec 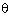 - cot
- cot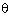 )2 =
)2 = 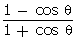
Solution

Q7. If 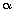 + β=900 and
+ β=900 and 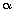 :β=2:1, then sin
:β=2:1, then sin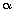 : sin β=
: sin β=
Solution
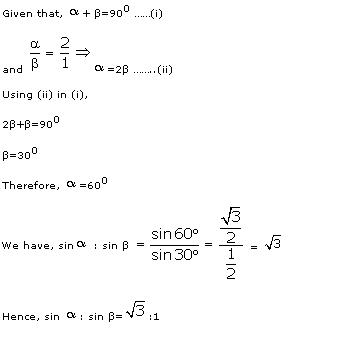
Q8. If 3 cos 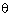 = 1, then the value of cosec
= 1, then the value of cosec 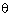 is :
is :
Solution
cos 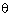 =
=  Let base = k and hypotenuse = 3k
Let base = k and hypotenuse = 3k
 Perpendicular =
Perpendicular = 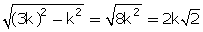
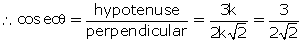
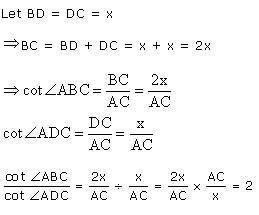
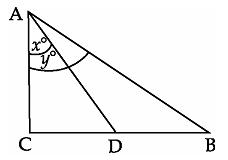
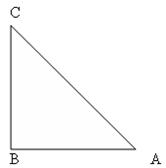
Q9. 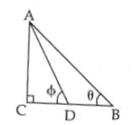 If figure, ABC is right angled triangle, right angled at C. D is mid-point of BC. Show that
If figure, ABC is right angled triangle, right angled at C. D is mid-point of BC. Show that 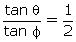
 If figure, ABC is right angled triangle, right angled at C. D is mid-point of BC. Show that
If figure, ABC is right angled triangle, right angled at C. D is mid-point of BC. Show that Solution
In  ABC,
ABC, 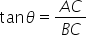 In
In  ACD,
ACD, 
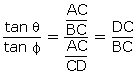
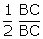
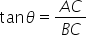 In
In 
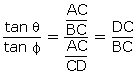
Q10. Without
using trigonometric table prove that:
tan
1o tan 11o tan 21o tan 69o tan 79o
tan 89o = 1
Solution
tan
1o tan 11o tan 21o tan 69o tan 79o
tan 89o
=
tan (90o - 89o) tan (90o - 79o)
tan (90o - 69o) tan 69o tan 79o tan 89o
=
cot 89o cot 79o cot 69o tan 69o
tan 79o tan 89o
=
cot 89o cot 79o cot 69o 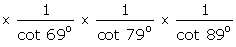 = 1
= 1
Q11. 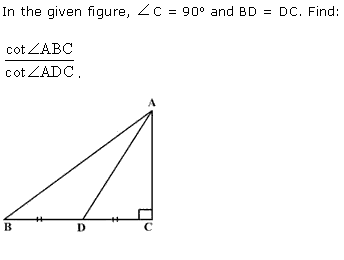
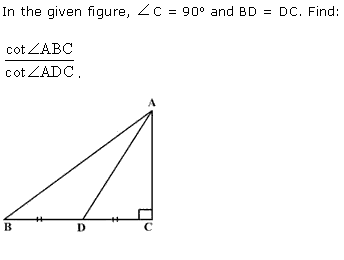
Solution
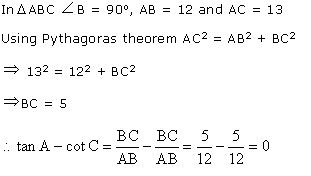
Q12. In figure, AC = 13 cm, BC = 12 cm, then sec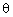 equals :
equals :
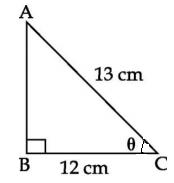

Solution
Q13. If 6 cot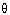 + 2 cosec
+ 2 cosec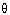 = cot
= cot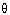 + 5 cosec
+ 5 cosec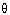 , then cos
, then cos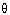 is:
is:
Solution
6 cot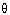 + 2 cosec
+ 2 cosec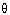 = cot
= cot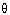 + 5 cosec
+ 5 cosec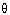 5 cot
5 cot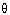 = 3 cosec
= 3 cosec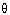
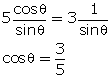
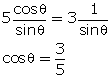
Q14. In figure, if D is mid-point of BC, the value of  is:
is:

Solution
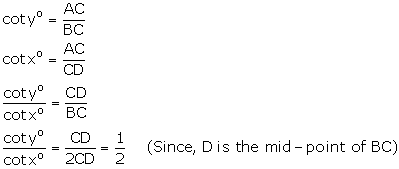
Q15. If tan 2A = cot (A - 18o), then the value of A is
Solution
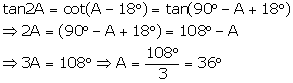
Q16. Find the length of the diagonals of the rhombus shown in the figure given below.
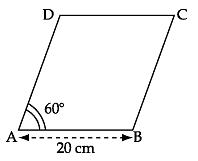

Solution
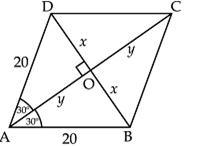 We know that the diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles.
In
We know that the diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles.
In 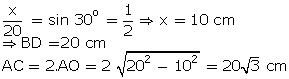
Q17. In the given figure find tan A - cot C. 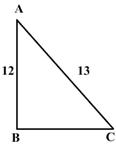

Solution
Q18. The value of  is equal to:
is equal to:
Solution
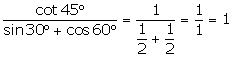
Q19. Prove
that: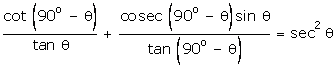 .
.
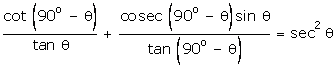 .
.Solution
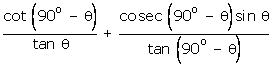
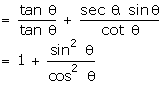 =
1 + tan2
=
1 + tan2
Q20. [cos4 A - sin4A] is equal to:
Solution
cos4 A - sin4A
= cos4 A - (1 - cos2A)2
= cos4 A - (1 + cos4A - 2 cos2A)
= 2 cos2 A - 1
Q21. Prove
that 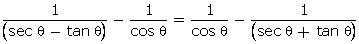
Solution
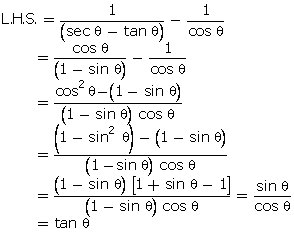
 Hence,
R.H.S. = L.H.S.
Hence,
R.H.S. = L.H.S.
Q22. If sin (A - B) = 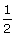 and cos (A + B) =
and cos (A + B) = 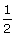 , then the value of B is:
, then the value of B is:
Solution
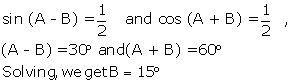
Q23. 
Solution

Q24. If 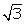 tan
tan 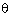 = 3 sin
= 3 sin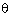 , prove that sin2
, prove that sin2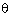 - cos2
- cos2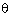 =
=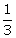 .
.
Solution
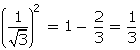 = RHS
= RHS
Q25. If x = 2 , y = 2 + 1, then the value of x + y is:
+ 1, then the value of x + y is:
Solution
Q26. If cos x = cos 60o cos 30o + sin 60o sin 30o, then the value of x is
Solution
cos x = cos 60o cos 30o + sin 60o sin 30o
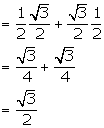 We know cos 30o =
We know cos 30o = 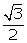 Hence, x = 30o
Hence, x = 30o
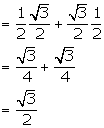 We know cos 30o =
We know cos 30o =
Q27.

Solution
Q28. Prove
that (sin A + cosec A)2 + (cos A + sec A)2 = 7 + tan2A
+ cot2A.
Solution
LHS
= (sin A + cosec A)2 + (cos
A + sec A)2
= sin2A
+ cosec2A + 2 sin A cosec A + cos2A + sec2A
+ 2cos A sec A
= 1 + 2
+ 2 + cosec2 A + sec2A
= 1 + 2
+ 2 + cot2 A + 1 + 1 + tan2A
= 7 +
cot2A + tan2A = RHS
Q29. sin (60o + 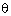 ) - cos (30o -
) - cos (30o - 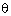 ) is equal to (where (60o +
) is equal to (where (60o + 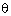 ) and (30o -
) and (30o - 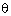 ) are both acute angles):
) are both acute angles):
Solution
sin (60o + 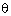 ) - cos (30o -
) - cos (30o - 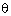 )
= sin (60o +
)
= sin (60o + 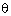 ) - cos (90o - (60o +
) - cos (90o - (60o + 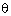 ))
= sin (60o +
))
= sin (60o + 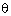 ) - sin (60o +
) - sin (60o + 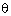 )
= 0
)
= 0
Q30. Prove that 1
+ 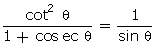
Solution
LHS = 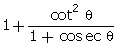 =
1 +
=
1 + 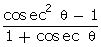 = 1 +
= 1 + 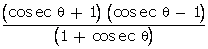 = 1 + cosec
= 1 + cosec 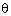 - 1 = cosec
- 1 = cosec 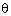 =
= 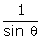 = RHS
= RHS
Q31. If 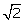 sin (60o -
sin (60o - 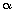 ) = 1, then
) = 1, then 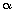 is:
is:
Solution
Q32. Prove
that 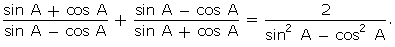
Solution
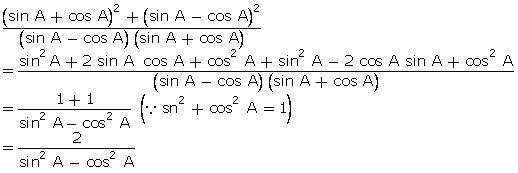
Q33. 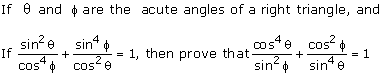
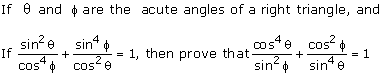
Solution
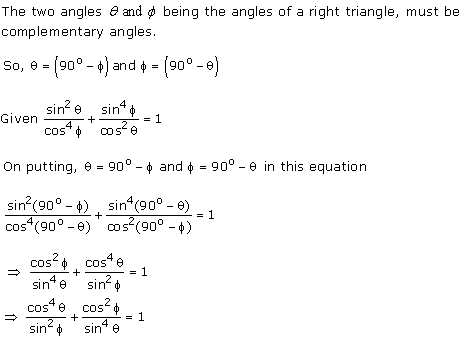
Q34. If tan
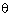 + sin
+ sin 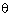 = m and tan
= m and tan 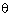 - sin
- sin 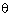 = n, show that
m2 - n2 = 4
= n, show that
m2 - n2 = 4 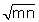
Solution
m2
- n2 = (m - n) (m + n)
= (2 sin 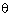 ) (2 tan
) (2 tan 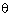 )
= 4 sin
)
= 4 sin 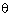 tan
tan 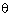 ...
(i)
mn
= (tan
...
(i)
mn
= (tan 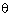 + sin
+ sin 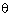 ) (tan
) (tan 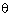 - sin
- sin 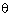 )
= tan2
)
= tan2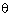 - sin2
- sin2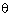

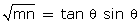 ... (ii)
(i)
and (ii)
... (ii)
(i)
and (ii) 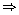 m2
- n2 = 4
m2
- n2 = 4 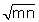 .
.

Q35. Prove
that cos8 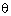 - sin8
- sin8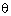 = (cos2
= (cos2 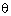 - sin2
- sin2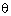 ) (1 - 2sin2
) (1 - 2sin2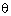 cos2
cos2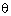 )
)
Solution

Q36. The value of  is
is
Solution
Q37. If
A, B, C are interior angles of 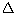 ABC, show that:
ABC, show that:
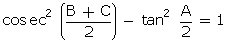
Solution
cosec2
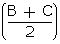 - tan2
- tan2
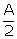 =
cosec2
=
cosec2 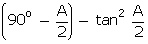
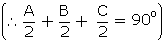 =
sec2
=
sec2 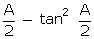 =
1
=
1 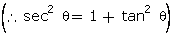
Q38. Prove:
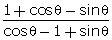 = cosec
= cosec 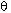 + cot
+ cot 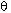
Solution
L.H.S. =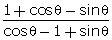


Q39. If x = r sin A cos C, y = r sin A
sin C, z = r cos A, prove that r2 = x2 + y2
+ z2.
Solution
x = r sinA cosC, y = r sinA sinC, z = r cosA
x2 + y2 + z2 =
r2 sin2A cos2C + r2 sin2A
sin2C + r2 cos2A
= r2 sin2A
(cos2C + sin2C) + r2 cos2A
= r2sin2A
+ r2cos2A
= r2(sin2A
+ cos2A)
= r2 (since,
sin2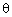 + cos2
+ cos2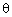 = 1)
= 1)
Q40. If sin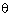 =
= 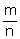 , find the value of
, find the value of 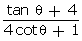
Solution
sin 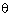 =
= 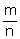
 tan
tan 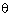 =
= 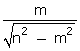
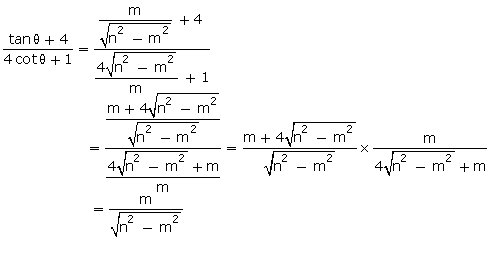
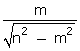
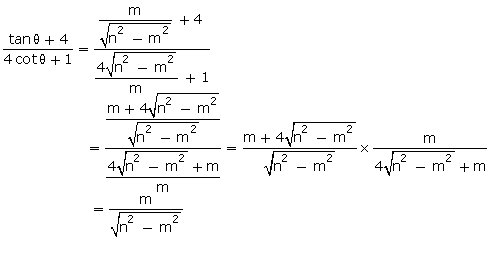
Q41. In figure below,  ABC is right-angled at B and tan A =
ABC is right-angled at B and tan A =  . If AC = 15 cm, then the length of AB is :
. If AC = 15 cm, then the length of AB is :
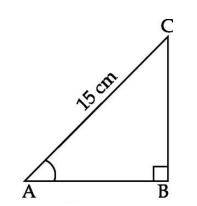

Solution
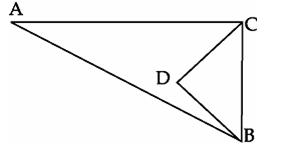
Q42. In the figure given below, 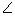 ACB = 90o,
ACB = 90o, 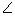 BDC = 90o, CD = 4 cm, BD = 3 cm, AC = 12 cm. cos A - sin A is equal to:
BDC = 90o, CD = 4 cm, BD = 3 cm, AC = 12 cm. cos A - sin A is equal to:

Solution
Applying Pythagoras theorem,
BC2 = CD2 + BD2 = (4 cm)2 + (3 cm)2
BC = 5 cm
AB2 = AC2 + BC2 = (12 cm)2 + (5 cm)2
AB = 13 cm
 cos A - sin A
cos A - sin A
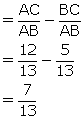
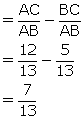
Q43. In the figure, if PS = 14 cm, the value of tan a is equal to:
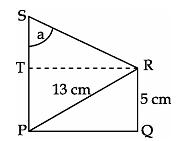

Solution
tan a = 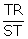 … (1)
ST = PS - TP = 14 cm - 5 cm = 9 cm
Using Pythagoras theorem in triangle PQR, we have:
(13)2 = PQ2 + (5)2
PQ2 = 169 - 25 = 144
PQ = 12 cm
TR = PQ = 12 cm
From (1),
tan a =
… (1)
ST = PS - TP = 14 cm - 5 cm = 9 cm
Using Pythagoras theorem in triangle PQR, we have:
(13)2 = PQ2 + (5)2
PQ2 = 169 - 25 = 144
PQ = 12 cm
TR = PQ = 12 cm
From (1),
tan a = 
Q44. If
x = a cos 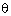 + b sin
+ b sin 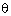 and y = b cos
and y = b cos 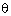 - a sin
- a sin 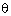 , then prove that x2 + y2 = a2
+ b2.
, then prove that x2 + y2 = a2
+ b2.
Solution
x
= a cos 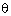 + b sin
+ b sin 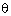 ...(1)
y
= b cos
...(1)
y
= b cos 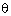 - a sin
- a sin 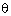 ...(2)
Squaring
and adding, we get,
x2
+ y2 = a2 cos2
...(2)
Squaring
and adding, we get,
x2
+ y2 = a2 cos2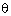 + b2 sin2
+ b2 sin2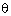 + 2ab sin
+ 2ab sin 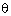 cos
cos 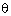 + b2
cos2
+ b2
cos2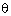 + a2
sin2
+ a2
sin2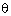 - 2ab sin
- 2ab sin 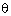 cos
cos 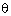 = a2 (sin2
= a2 (sin2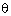 + cos2
+ cos2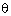 ) + b2(sin2
) + b2(sin2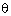 + cos2
+ cos2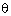 )
= a2 + b2
Hence,
proved
)
= a2 + b2
Hence,
proved
Q45. The value of cos θ cos(90° - θ) - sin θ sin (90° - θ) is:
Solution
cos θ cos(90° - θ) - sin θ sin (90° - θ)
= cos θ sin θ - sin θ cos θ
= 0
Q46. If sin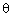 = cos
= cos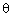 , then value of
, then value of 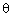 is :
is :
Solution
Given, 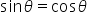 We know
We know  Thus,
Thus,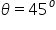
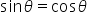 We know
We know  Thus,
Thus,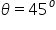
Q47. The value of 5 tan2 - 5 sec2
- 5 sec2  is:
is:
Solution
5 tan2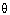 - 5 sec2
- 5 sec2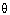 =5 tan2
=5 tan2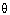 - 5 (1 + tan2
- 5 (1 + tan2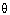 )
= 5 tan2
)
= 5 tan2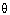 - 5 - 5 tan2
- 5 - 5 tan2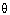 = -5
= -5
Q48. If sin θ + cos θ = 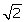 sin (90° - θ), then find the value of tan θ.
sin (90° - θ), then find the value of tan θ.
Solution

Q49. [(sec A + tan A) (1 - sin A)] on simplification gives:
Solution
(sec A + tan A) (1 - sin A)


Q50. Without using trigonometric tables, prove that


Solution

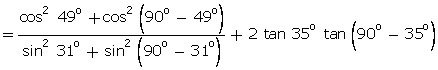
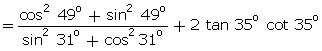 = 1 + 2
= 1 + 2
Q51. From the figure, the value of cosec A + cot A is :
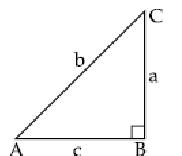

Solution
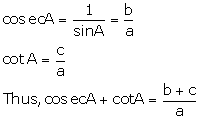
Q52. If cot A =  , then the value of (sin A + cos A)
, then the value of (sin A + cos A)  cosec A is :
cosec A is :
Solution
Q53. If cosec2 (1 + cos
(1 + cos ) (1 - cos
) (1 - cos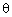 ) =
) = 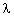 , then the value of
, then the value of 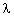 is:
is:
Solution
Q54. The maximum value of 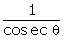 is:
is:
Solution
We know 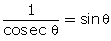 and the maximum value of sin
and the maximum value of sin 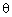 is 1.
Hence, the maximum value of
is 1.
Hence, the maximum value of 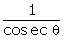 is 1.
is 1.
Q55. If
A, B, C are interior angles of  ABC, show that:
ABC, show that:
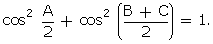
Solution
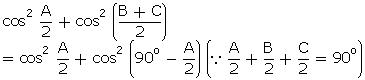 =
=
Q56. If cos (40o + A) = sin 30o, the value of A is:
Solution
cos (40o + A) = sin 30o
cos (40o + A) = sin (90 - 60o)
cos (40o + A) = cos 60o
40o + A = 60o
A = 20o
Q57. 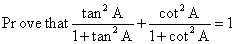
Solution

Q58. Without using trigonometric tables, prove that:
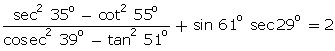
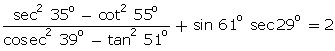
Solution
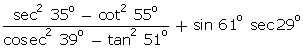
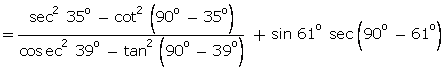
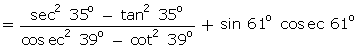
Q59. Given that sin A = 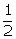 and cos B =
and cos B = 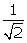 then the value of A + B is:
then the value of A + B is:
Solution
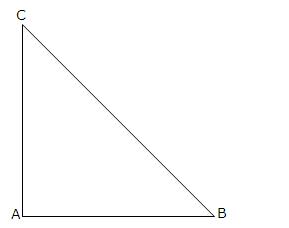
Q60.  ABC is right angled at A, the value of tan B
ABC is right angled at A, the value of tan B  tan C is:
tan C is:
Solution
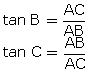
Q61. If
cosec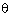 = x +
= x + 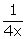 , prove that:
cosec
, prove that:
cosec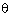 + cot
+ cot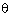 = 2x or
= 2x or 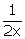
Solution
We
know: 1 + cot2 = cosec2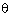 cot2
cot2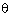 = cosec2
= cosec2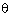 - 1
cot2
- 1
cot2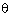 =
= 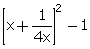 = x2 +
= x2 + 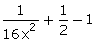 = x2 +
= x2 +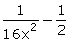 =
= 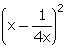 cot
cot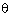 =
= 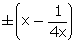 cot
cot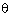 = x -
= x - 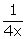 or cot
or cot 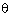 = -x +
= -x + 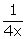
 cosec
cosec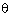 + cot
+ cot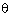 = 2x or cosec
= 2x or cosec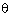 + cot x =
+ cot x = 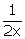
Q62. 

Solution

Q63. Prove the following trigonometric identities.


Solution

Q64. Prove
that sin A(1 + tan A) + cos A (1 + cot A) = sec A + cosec A.
Solution
LHS
= sin A(1 + tan A) + cos A (1 + cot A)
= sin A 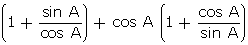


Q65. Prove
that 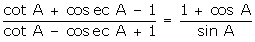
Solution

Q66. If sin (20o + 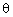 ) = cos 30o, then the value of
) = cos 30o, then the value of 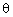 is:
is:
Solution
sin (20o + 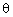 ) = cos 30o
We know cos 30o =
) = cos 30o
We know cos 30o = 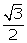
 sin (20o +
sin (20o + 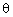 ) =
) = 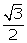 = sin 60o
= sin 60o
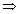 20o +
20o + 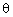 = 60o
= 60o
 = 40o
= 40o
Q67. Find the value of tan 60o geometrically.
Solution
Consider an equilateral  ABC and let a be the length of each side of
ABC and let a be the length of each side of  ABC.
AB = BC = CA = a
ABC.
AB = BC = CA = a
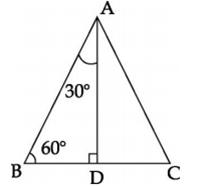 Draw AD
Draw AD  BC
BC
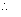
 ABD
ABD 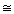
 ACD
ACD
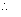 BD = DC
BD = DC  BD =
BD = 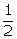 BC =
BC = 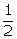 a
and
a
and 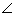 BAD =
BAD = 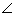 CAD
CAD 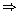
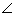 BAD =
BAD = 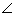 CAD = 30o
Using Pythagoras theorem in
CAD = 30o
Using Pythagoras theorem in 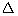 ABD,
AD2 = AB2 - BD2
ABD,
AD2 = AB2 - BD2
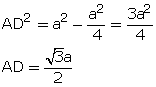
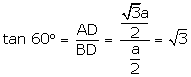
 Draw AD
Draw AD 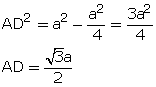
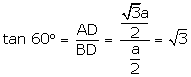
Q68. Given that cos  =
=  then tan
then tan is equal to
is equal to
Solution

Q69. In figure below sec  is:
is:
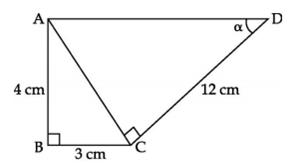

Solution
Using Pythagoras theorem in  ABC,
ABC,
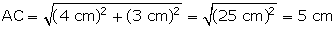 Using Pythagoras theorem in
Using Pythagoras theorem in 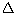 ACD,
ACD,
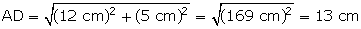
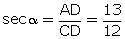
Q70. Prove
that : (sin + cosec
+ cosec )2 + (cos
)2 + (cos + sec
+ sec )2 = 7 + tan2
)2 = 7 + tan2 + cot2
+ cot2
Solution
LHS
= (sin + cosec
+ cosec )2 + (cos
)2 + (cos + sec
+ sec )2
= sin2
)2
= sin2 + cosec2
+ cosec2 + 2sin
+ 2sin cosec
cosec + cos2
+ cos2 + sec2
+ sec2 + 2cos
+ 2cos sec
sec = sin2
= sin2 + cos2
+ cos2 + 2 + 2 + cosec2
+ 2 + 2 + cosec2 + sec2
+ sec2 = 1 + 4 + (1 + cot2
= 1 + 4 + (1 + cot2 ) + (1 + tan2
) + (1 + tan2 )
= 7 + tan2
)
= 7 + tan2 + cot2
+ cot2 = RHS
= RHS
Q71. In 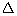 ABC, right angled at B, if cot A=
ABC, right angled at B, if cot A= 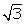 then the value of cos A
then the value of cos A 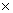 sin C + sin A
sin C + sin A 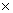 cos C
cos C
Solution
 Given that, cot A =
Given that, cot A =
Q72. If cos A + cos2 A = 1, then sin2 A + sin4 A is
Solution
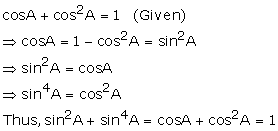
Q73. If  and f are the acute angles of a right triangle,
and
and f are the acute angles of a right triangle,
and 
Solution
The two angles  and f being
the acute angles of a right triangle must be complementary angles.
So,
and f being
the acute angles of a right triangle must be complementary angles.
So, 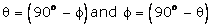
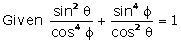 Substituting,
Substituting, 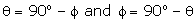 in above
equation,
in above
equation,
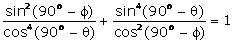
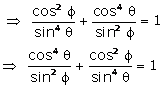
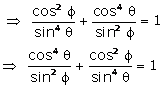
Q74. 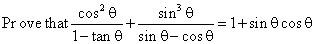
Solution

Q75. Given 15cot A = 8, find sin A and sec A.
Solution
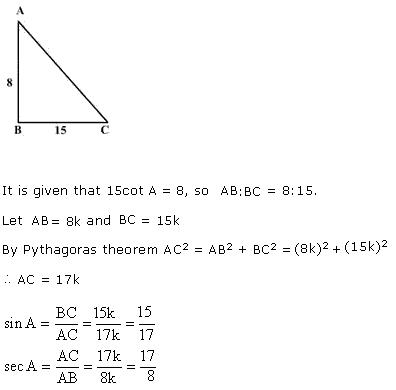
Q76. Prove
that 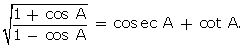
Solution

Q77. If
sin 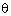 + sin2
+ sin2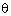 = 1, then find the value of cos2
= 1, then find the value of cos2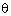 + cos4
+ cos4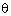 .
.
Solution
sin
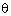 + sin2
+ sin2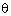 = 1
= 1
 sin
sin 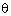 = 1 - sin2
= 1 - sin2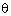 = cos2
= cos2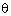
 sin2
sin2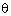 = cos4
= cos4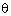
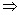 1 - cos2
1 - cos2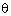 = cos4
= cos4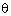
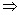 cos2
cos2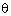 + cos4
+ cos4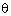 = 1
= 1
Q78. Prove
that:
cos sin
sin -
- 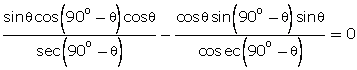
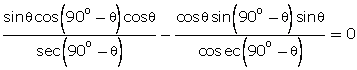
Solution
LHS
= cos sin
sin -
- 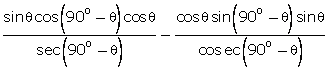 =
cos
=
cos sin
sin -
- 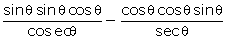 =
cos
=
cos sin
sin - sin3
- sin3 cos
cos - cos3
- cos3 sin
sin =
cos
=
cos sin
sin - sin
- sin cos
cos (sin2
(sin2 + cos2
+ cos2 )
=
cos
)
=
cos sin
sin - sin
- sin cos
cos
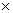 1 [Since, sin2
1 [Since, sin2 + cos2
+ cos2 = 1]
=
0 = RHS
= 1]
=
0 = RHS
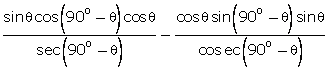 =
cos
=
cos
Q79. If x = 3 sec2 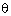 - 1, y = tan2
- 1, y = tan2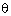 - 2 then x - 3y is equal to
- 2 then x - 3y is equal to
Solution
x = 3 sec2 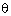 - 1, y = tan2
- 1, y = tan2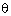 - 2
x - 3y = 3 sec2
- 2
x - 3y = 3 sec2 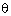 - 1 - 3tan2
- 1 - 3tan2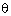 + 6
= 3(1) + 5 = 8
(Since, sec2
+ 6
= 3(1) + 5 = 8
(Since, sec2 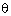 - tan2
- tan2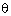 = 1)
= 1)
Q80. Prove
that:
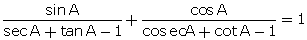
Solution
 =
1 = RHS
=
1 = RHS
Q81. If x. tan 45o. cot60o = sin 30o. cosec60o, then the value of x is:
Solution
x. tan 45o. cot60o = sin 30o. cosec60o
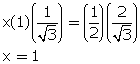
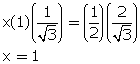
Q82. 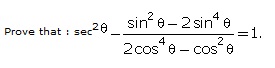
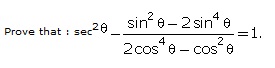
Solution
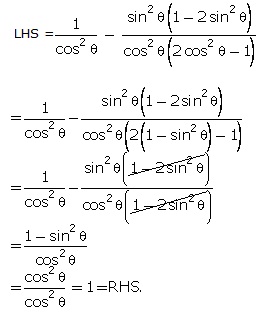
Q83.  ABC is a right triangle right angled at
ABC is a right triangle right angled at 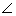 C, then the value cosec2A - tan2B is :
C, then the value cosec2A - tan2B is :
Solution
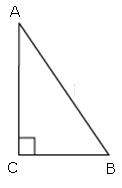 cosec2A - tan2B
cosec2A - tan2B

Q84. If 7 sin2 q
+ 3 cos2 q = 4, then prove that sec q + cosec q
= 2 +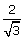 .
.
Solution
7 sin2 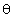 + 3 cos2
+ 3 cos2
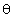 = 4
7 sin2
= 4
7 sin2 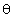 + 3 (1 - sin2
+ 3 (1 - sin2 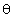 ) = 4
sin
) = 4
sin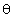 =
= 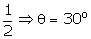 sec 30o + cosec30o
=
sec 30o + cosec30o
= 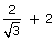
Q85. If 5
tan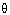 = 4, find the value of
= 4, find the value of 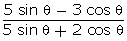
Solution
5
tan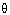 = 4
= 4
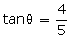
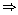 5 sin
5 sin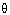 = 4 cos
= 4 cos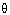
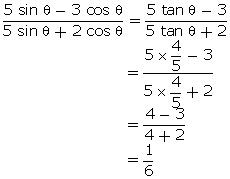
Q86. Prove
that:
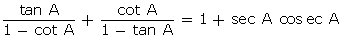
Solution

Q87. Prove
that (cosec A - sin A) (sec A - cos A) = 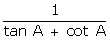
Solution
LHS
= (cosec A - sin A) (sec A -
cos A) 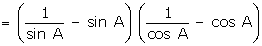
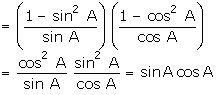 RHS
=
RHS
= 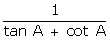
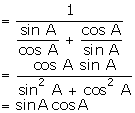 Hence,
LHS = RHS
Hence,
LHS = RHS
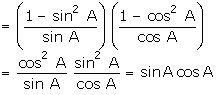 RHS
=
RHS
= 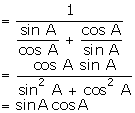 Hence,
LHS = RHS
Hence,
LHS = RHS
Q88. If
sin (A + B) = cos (A - B) = 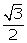 and A,B
(A >B) are acute angles, find the
value of A and B.
and A,B
(A >B) are acute angles, find the
value of A and B.
Solution
Given,
sin (A + B) = cos (A - B) = 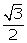 Therefore,
A
+ B = 60o ; A - B = 30o
Solving
for A and B, we get,
A
= 45o and B = 15o
Therefore,
A
+ B = 60o ; A - B = 30o
Solving
for A and B, we get,
A
= 45o and B = 15o
Q89. If
tan  + sin
+ sin  = m and tan
= m and tan  - sin
- sin  = n
Show
that (m2 - n2)2 = 16 mn
= n
Show
that (m2 - n2)2 = 16 mn
Solution
tan
 + sin
+ sin  = m
tan
= m
tan
 - sin
- sin  = n
(m
+ n) (m - n) = 2 tan
= n
(m
+ n) (m - n) = 2 tan 
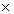 2 sin
2 sin  m2
- n2 = 4 tan
m2
- n2 = 4 tan  sin
sin  L.H.S.
= (m2 - n2)2
= 16 tan2
L.H.S.
= (m2 - n2)2
= 16 tan2  sin2
sin2
 R.H.S.
= 16 mn = 16 (tan
R.H.S.
= 16 mn = 16 (tan  + sin
+ sin  ) (tan
) (tan  - sin
- sin  )
= 16 (tan2
)
= 16 (tan2  - sin2
- sin2
 )
= 16
)
= 16 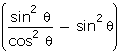 = 16
= 16 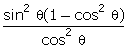 = 16
= 16 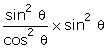 = 16 tan2
= 16 tan2  sin2
sin2
 L.H.S.
= R.H.S.
L.H.S.
= R.H.S.
 (m2 - n2)2 = 16mn
(m2 - n2)2 = 16mn
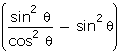 = 16
= 16 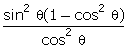 = 16
= 16 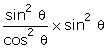 = 16 tan2
= 16 tan2
Q90. If
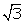 tan
tan 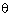 = 3 sin
= 3 sin 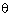 , find the value of sin2
, find the value of sin2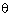 - cos2
- cos2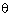
Solution
Q91. If A, B, C are the interior angles of ΔABC, then prove that
 .
.
 .
.Solution

Q92. If 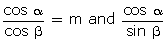 = n then
Show that (m2 + n2) cos2
= n then
Show that (m2 + n2) cos2
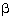 = n2.
= n2.
Solution
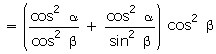
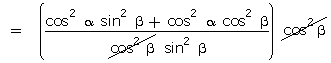
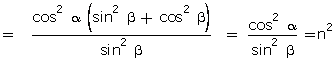
Q93. If
3 cot A = 4, find the value of 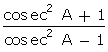
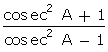
Solution
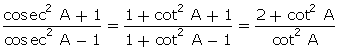
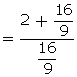
Q94. If cos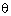 =
=  , then the value of cos
, then the value of cos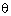 [cos
[cos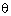 - sec
- sec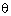 ] is:
] is:
Solution
cos 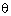 =
= 
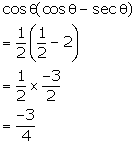
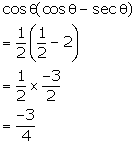
Q95. Evaluate:
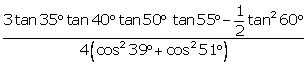
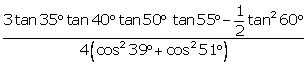
Solution
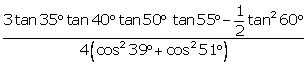
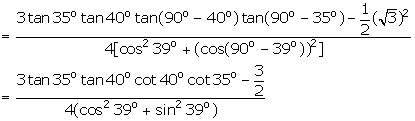
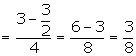
Q96. Prove that 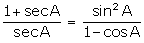 .
.
Solution
LHS = 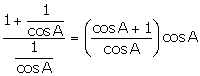 = 1 + cos A
= 1 + cos A
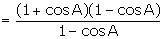
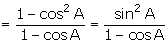 = RHS
= RHS
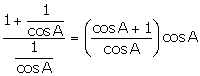 = 1 + cos A
= 1 + cos A
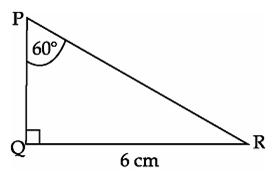
Q97. In fig.,  PQR is right angled at Q, QR = 6 cm
PQR is right angled at Q, QR = 6 cm  QPR = 60o. Find the length of PQ and PR.
QPR = 60o. Find the length of PQ and PR.

Solution
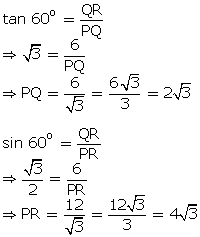
Q98. 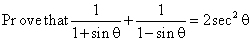
Solution

Q99. Prove
that
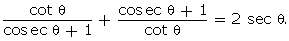
Solution

Q100. In triangle ABC, right angled at A, if AB = 5, AC = 12 and BC = 13, find sin B, cos C and tan B.
Solution
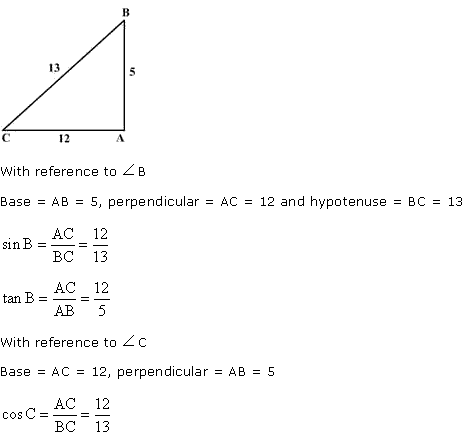
Q101. Evaluate:


Solution

Q102. If sin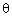 =
=  , then the value of sin
, then the value of sin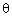 (sin
(sin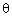 - cosec
- cosec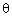 ) is
) is
Solution
Q103. Prove
that 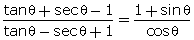
Solution
L.H.S
= 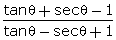


Q104. Prove:
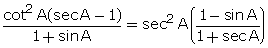
Solution

Q105. If a cot θ+ b cosec θ = p and b cot θ + a cosec θ= q then p2 - q2 is equal to
Solution
p = a cot θ + b cosec θ
q = b cot θ + a cosec θ
p2 - q2 = (a cot θ + b cosec θ)2 - (b cot θ + a cosec θ)2
= a2 cot2 θ + b2 cosec2 θ + 2ab cot θ cosec θ - b2 cot2 θ - a2 cosec2 θ - 2ab cot θ cosec θ
= a2 (cot2 θ - cosec2 θ) + b2 (cosec2 θ - cot2 θ)
= b2 - a2
(Since, cosec2 A - cot2 A = 1)
Q106. 
Solution
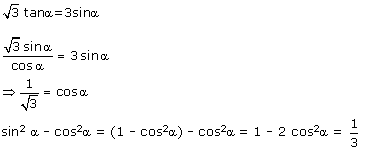
Q107. If
tan (A + B) = 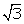 and tan (A - B) =
and tan (A - B) = 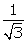 , 0o < A + B
, 0o < A + B 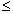 90o;
A > B find A and B.
90o;
A > B find A and B.
Solution
Given,
tan (A + B) = 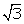 and tan (A - B) =
and tan (A - B) = 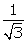 Therefore,
A
+ B = 60o; A - B = 30o
Solving
the two equations, we get,
A
= 45o ; B = 15o
Therefore,
A
+ B = 60o; A - B = 30o
Solving
the two equations, we get,
A
= 45o ; B = 15o
Q108. Prove
that tan2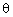 + cot2
+ cot2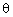 + 2 = sec2
+ 2 = sec2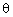 cosec2
cosec2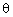
Solution
 = cosec2
= cosec2
Q109. If
cos 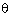 - sin
- sin 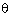 =
= 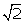 sin
sin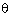 , prove that cos
, prove that cos 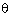 + sin
+ sin 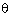 =
= 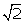 cos
cos 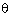 .
.
Solution
Given
cos 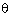 - sin
- sin 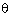 =
= 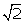 sin
sin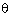
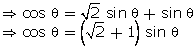

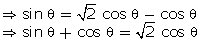

Q110. If sec
4A = cosec (A - 20o) where 4 A is an acute angle, fine the value
of A.
Solution
Given,
sec 4A = cosec (A - 20o)
Since,
sec 4 A = cosec (90o - 4 A)
(90o
- 4 A) and (A - 20o) are acute angles
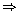 90o - 4 A = A - 20o
90o - 4 A = A - 20o
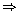 A = 22o
A = 22o
Q111. Prove
that:
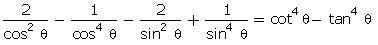
Solution
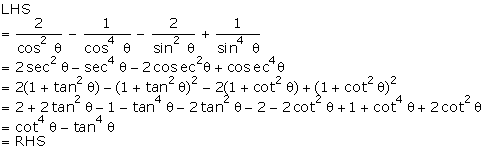
Q112. 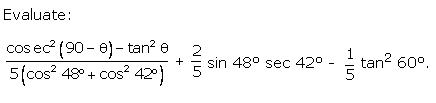
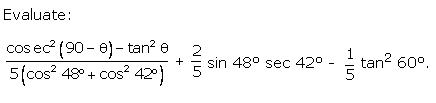
Solution
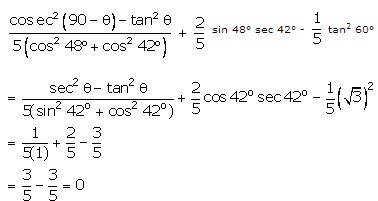
Q113. Prove that:
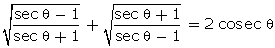
Solution
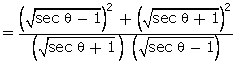
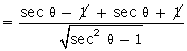
Q114. If a
cos 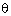 - b sin
- b sin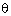 = c, prove that
(a sin
= c, prove that
(a sin
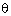 + b cos
+ b cos 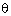 ) =
) = 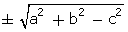 .
.
Solution
(a
cos 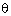 - b sin
- b sin 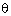 )2 = c2
a2
cos2
)2 = c2
a2
cos2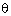 + b2 sin2
+ b2 sin2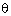 - 2 ab sin
- 2 ab sin 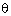 . cos
. cos 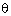 = c2
a2
(1 - sin2
= c2
a2
(1 - sin2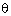 ) + b2 (1 - cos2
) + b2 (1 - cos2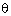 ) - 2 ab sin
) - 2 ab sin 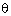 . cos
. cos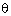 = c2
a2
+ b2 - c2 = (a sin
= c2
a2
+ b2 - c2 = (a sin 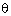 + b cos
+ b cos 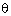 )2
(a
sin
)2
(a
sin 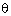 + b cos
+ b cos 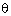 ) =
) = 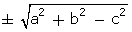
Q115. 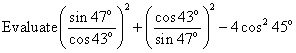
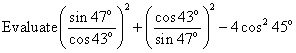
Solution
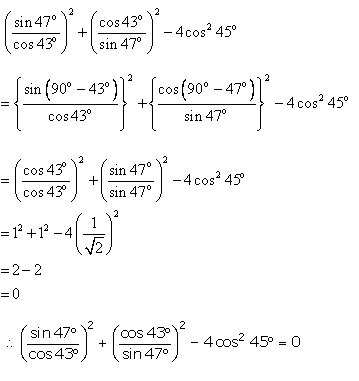
Q116. Prove
that 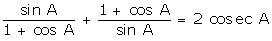 .
.
Solution
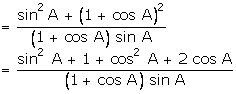
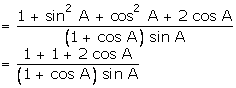

Q117. Evaluate:


Solution

Q118. If sin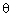 + cos
+ cos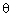 = m and sec
= m and sec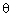 +cosec
+cosec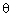 = n, prove
that n (
= n, prove
that n (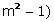 = 2m.
= 2m.
Solution
Given: sin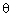 + cos
+ cos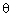 = m and sec
= m and sec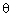 + cosec
+ cosec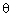 = n
Consider L.H.S. = n
= n
Consider L.H.S. = n 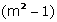 =
=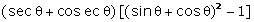 =
=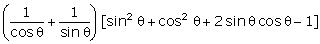 =
=
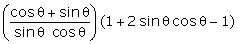
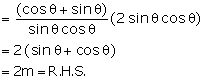
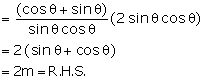
Q119. Prove
that 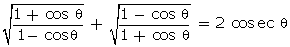
Solution
L.H.S.
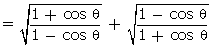
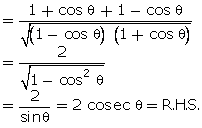
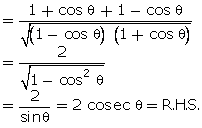
Q120. Evaluate cos 30o cos 45o - sin 30o sin 45o.
Solution
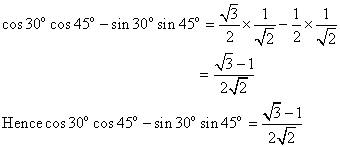
Q121. In  , right angled at Q, PR + QR = 25 cm and PQ = 5 cm. Find the value of sin P.
, right angled at Q, PR + QR = 25 cm and PQ = 5 cm. Find the value of sin P.
Solution
 Given, PR + QR = 25 cm and PQ = 5 cm
In right
Given, PR + QR = 25 cm and PQ = 5 cm
In right
Q122. Prove that 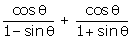 = 2 sec
= 2 sec 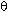 .
.
Solution
LHS = 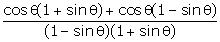
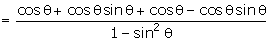
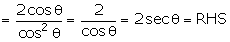
Q123. If A +
B = 90o, then prove that 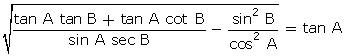
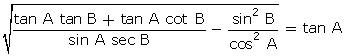
Solution

Q124. Prove
that:
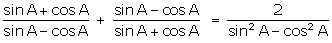
Solution
Q125. Evaluate:


Solution

Q126. Prove
the following identity:
(sin
 + sec
+ sec  )2 + (cos
)2 + (cos  + cosec
+ cosec  )2 = (1 + sec
)2 = (1 + sec  cosec
cosec  )2.
)2.
Solution
Consider
L.H.S. = (sin  + sec
+ sec  )2 + (cos
)2 + (cos  + cosec
+ cosec  )2
=
sin2
)2
=
sin2 + sec2
+ sec2  + 2 tan
+ 2 tan  + cos2
+ cos2
 + cosec2
+ cosec2 + 2 cot
+ 2 cot 
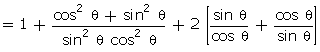
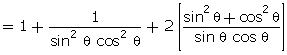 =
1 + sec2
=
1 + sec2 cosec2
cosec2 + 2 sec
+ 2 sec  cosec
cosec  =
(1 + sec
=
(1 + sec  cosec
cosec  )2 = R.H.S
)2 = R.H.S
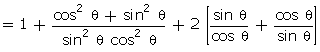
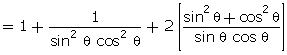 =
1 + sec2
=
1 + sec2
Q127. 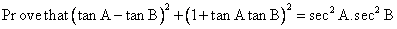
Solution

Q128. Prove the following:
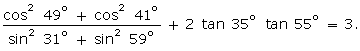
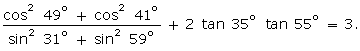
Solution
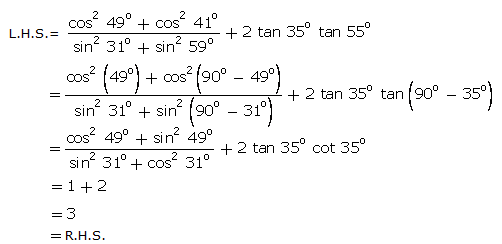
Q129. Prove
that 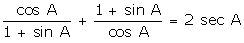
Solution
 = 2 sec A = RHS
= 2 sec A = RHS
Q130. 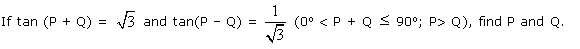
Solution
Q131. 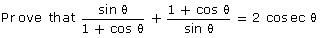
Solution

Q132. Prove that tan 1o tan 2o tan 3o ... tan 89o = 1
Solution
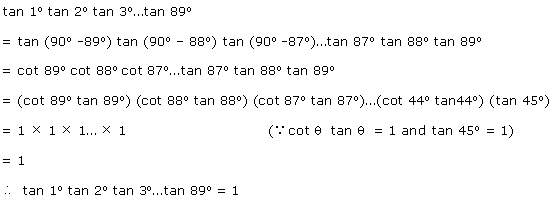
Q133. 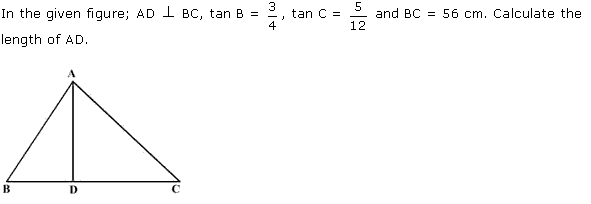
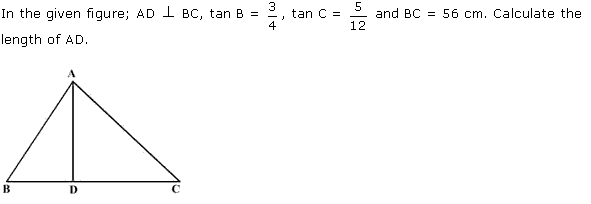
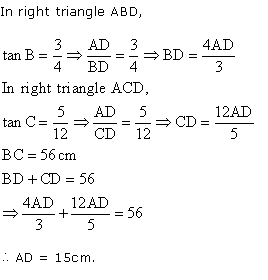
Solution
Q134. Prove that sec4 A - sec2 A = tan4 A + tan2 A
Solution
L.H.S = sec4 A - sec2 A = sec2 A (sec2 A - 1) = (1 + tan2 A) (tan2 A) = tan2 A + tan4 A= R.H.SHence sec4 A - sec2 A = tan4 A + tan4 A
Q135. Prove
that:
sec2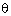 + cot2 (90o -
+ cot2 (90o - 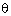 ) = 2 cosec2 (90o -
) = 2 cosec2 (90o - 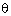 ) - 1
) - 1
Solution
L.H.S
= sec2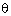 + cot2 (90o -
+ cot2 (90o - 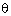 )
=
sec2
)
=
sec2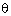 + tan2
+ tan2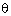 =
sec2
=
sec2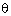 + sec2 - 1
=
2sec2
+ sec2 - 1
=
2sec2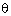 - 1
=
2 cosec2‑ (90o -
- 1
=
2 cosec2‑ (90o - 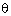 ) - 1
) - 1
Q136. Prove that 2(cos30o + sin 60o) = 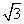 (1+ cos 60o + sin30o).
(1+ cos 60o + sin30o).
Solution
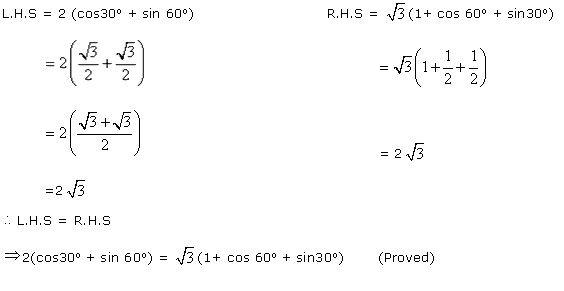
Q137. 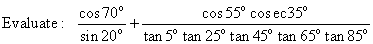
Solution

Q138. 
Solution
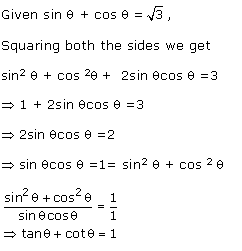
Q139. Given
that sin (A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B, find the value of sin 75o.
Solution
Given,
sin (A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B
sin
75o = sin (45o + 30o) = sin 45o
cos 30o + cos 45o sin 30o
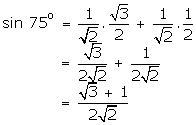
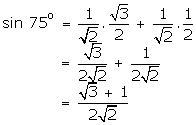
Q140. Evaluate: 2sin2 30o - 3cos2 45o + tan2 60o
Solution
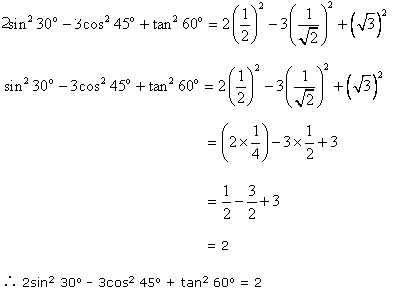
Q141. If
cosec (A - B) = 2, cot (A + B) = 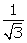 ,
0o < (A + B)
,
0o < (A + B) 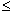 90o,
A > B, then find A and B.
90o,
A > B, then find A and B.
Solution
cosec
(A - B) = 2
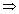 sin(A
- B) =
sin(A
- B) = 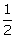
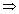 A - B = 30o … (1)
cot
(A + B) =
A - B = 30o … (1)
cot
(A + B) = 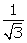
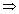 A + B = 60o … (2)
Solving
(1) and (2), we get,
A
= 45o and B = 15o
A + B = 60o … (2)
Solving
(1) and (2), we get,
A
= 45o and B = 15o
Q142. 
Solution
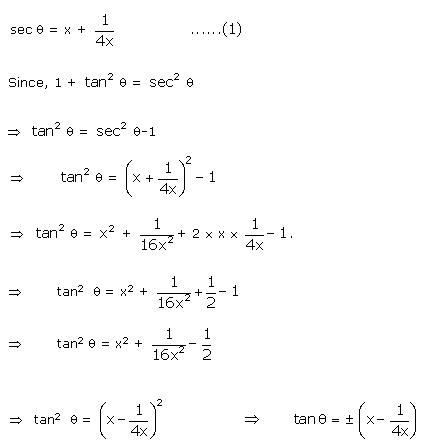
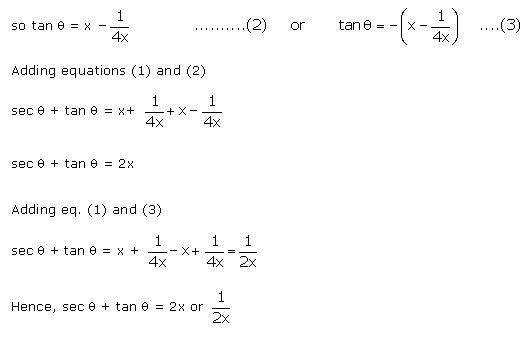
Q143. Prove
that 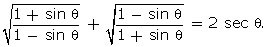
Solution
 = 2 sec
= 2 sec
Q144. If tan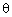 =
= 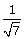 , find the value of
, find the value of 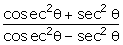 .
.
Solution
tan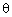 =
= 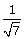 (given)
(given)
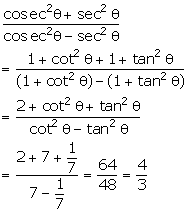
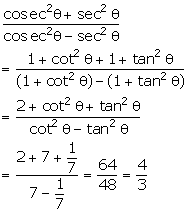
Q145. Prove
that:
(1 +
cot 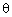 - cosec
- cosec 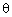 ) (1 + tan
) (1 + tan 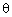 + sec
+ sec 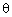 ) = 2
) = 2
Solution
(1
+ cot 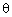 - cosec
- cosec 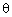 ) (1 + tan
) (1 + tan 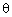 + sec
+ sec 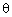 )
)
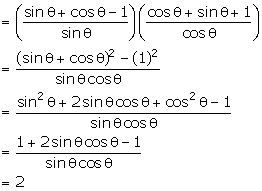
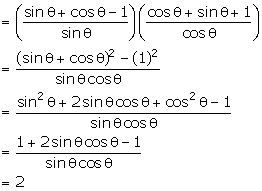
Q146. Prove
that 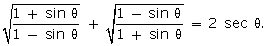
Solution

Q147. If 5
tan 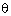 = 4, find the
value of
= 4, find the
value of 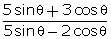
Solution
5
tan 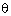 = 4
= 4
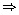 tan
tan 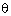 =
= 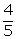
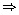
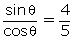
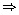 5 sin
5 sin 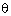 = 4 cos
= 4 cos 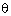
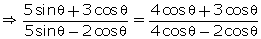 =
=
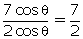
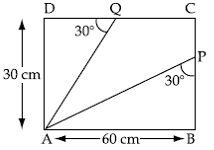
Q148. In figure ABCD is rectangle in
which segments AP and AQ are drawn. Find the length (AP + AQ).

Solution
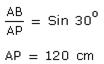
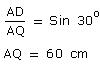 AP + AQ = 120 cm + 60 cm =
180 cm
AP + AQ = 120 cm + 60 cm =
180 cm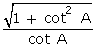
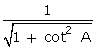
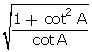
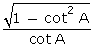
Comments
Post a Comment