Q1. If the two zeroes of the quadratic polynomial 7x2 - 15x - k are reciprocals of each other, the value of k is:
Solution
We know that if the roots are reciprocal of each other leads to product of the roots being equal to 1.
The product of roots = 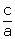
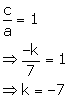
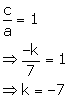
Q2. Find the zeros of the polynomial f(x) = 6x2 - 3
Solution
f(x) = 6x2 - 3
= 3(2x2 - 1)
=  The zeros of f(x) are given by f(x) = 0
That is
The zeros of f(x) are given by f(x) = 0
That is  = 0
= 0

 Hence the zeros of f(x) = 6x2 - 3 are:
Hence the zeros of f(x) = 6x2 - 3 are:  and
and  .
.
 The zeros of f(x) are given by f(x) = 0
That is
The zeros of f(x) are given by f(x) = 0
That is  = 0
= 0

 Hence the zeros of f(x) = 6x2 - 3 are:
Hence the zeros of f(x) = 6x2 - 3 are:  and
and  .
.
Q3. If 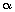 and
and 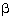 are the zeroes of the polynomial 4x2 + 3x + 7, then
are the zeroes of the polynomial 4x2 + 3x + 7, then 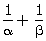 is equal to:
is equal to:
Solution

Q4. If α, ß are zeroes of polynomial f(x) = x2 + px + q then polynomial having 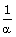 and
and 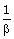 as its zeroes is :
as its zeroes is :
Solution

Q5. Find the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial 4x2 - 7.
Solution
4x2 - 7
= (2x)2 -  =
= 
 are the zeroes of the given polynomial.
are the zeroes of the given polynomial.
 =
= 
 are the zeroes of the given polynomial.
are the zeroes of the given polynomial.
Q6. Form a quadratic polynomial whose one of the zeroes is -15 and sum of the zeroes is 42.
Solution
One
of the zero = -15
Sum
of the zeroes = 42
 Other zero = 42 + 15 = 57
Product of the zeroes = 57
Other zero = 42 + 15 = 57
Product of the zeroes = 57  (-15) = -855
(-15) = -855
 The quadratic polynomial is
x2 - (sum of zeroes)x +
product of zeroes
i.e.,
x2 - 42x - 855
The quadratic polynomial is
x2 - (sum of zeroes)x +
product of zeroes
i.e.,
x2 - 42x - 855
Q7. If (x + 1) is a factor of x2 - 3ax + 3a - 7, then the value of a is:
Solution
Given, (x + 1) is a factor of x2 - 3ax + 3a - 7.
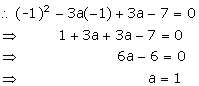
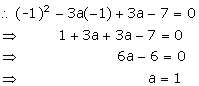
Q8. What must be added to f(x) = 6x5 + 5x4 + 11x3 - 3x2 + x + 5 so that it may be exactly divisible by g(x) = 3x2 - 2x + 4?
Solution

Q9. If the polynomial p(x) is divisible by x - 4, and 2 is a zero of p(x), then find p(x).
Solution
Since, 2 is a zero of p(x), (x - 2) is a factor of p(x).
Also, given that (x - 4) is a factor of p(x).
Using Division Algorithm, we get
p(x) = (x - 2) (x - 4) = x2 - 6x+ 8
Q10. From a quadratic polynomial whose one of the zeroes is -15 and sum of the zeroes is 42.
Solution
One of the zero = -15
Sum of the zeroes = 42
Let the other zero be x.
 -15 + x = 42
-15 + x = 42
 x = 42 + 15 = 57
Product of the zeroes = 57
x = 42 + 15 = 57
Product of the zeroes = 57  (-15) = -855
(-15) = -855
 The required quadratic polynomial is
x2 - 42x - 855
The required quadratic polynomial is
x2 - 42x - 855
 x = 42 + 15 = 57
Product of the zeroes = 57
x = 42 + 15 = 57
Product of the zeroes = 57
Q11. The remainder on dividing x3 + 2x2 + kx + 3 by x - 3 is 21. Sanju was asked to find the quotient. He was a little puzzled and was thinking how to proceed. His classmate gunjan helped him by suggesting that he should first find k and then proceed further.
Explain how the question was solved.
Solution
Let p(x) = x3 + 2x2 + kx + 3
Using Remainder theorem, we have:
p(3) = 33 + 2  32 + 3k + 3 = 21
32 + 3k + 3 = 21
 k = -9
Thus, p(x) = x3 + 2x2 - 9x + 3
k = -9
Thus, p(x) = x3 + 2x2 - 9x + 3
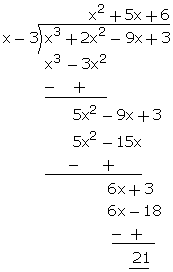 When p(x) is divided by (x - 3), the quotient is x2 + 5x + 6.
When p(x) is divided by (x - 3), the quotient is x2 + 5x + 6.
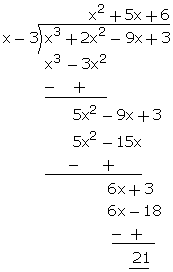 When p(x) is divided by (x - 3), the quotient is x2 + 5x + 6.
When p(x) is divided by (x - 3), the quotient is x2 + 5x + 6.
Q12. If (x + 1) is a factor of 2x3 + ax2 + 2bx + 1, then find the values of a and b given that 2a - 3b = 4.
Solution
Since, (x + 1) is a factor of f(x) = 2x3 + ax2 + 2bx + 1,
f(-1) = 0
 -2 + a - 2b + 1 =0
-2 + a - 2b + 1 =0
 a - 2b = 1...(1)
Given, 2a - 3b = 4...(2)
Solving (1) and (2), we get,
a = 5
b = 2
a - 2b = 1...(1)
Given, 2a - 3b = 4...(2)
Solving (1) and (2), we get,
a = 5
b = 2
Q13. If the polynomial f(x) = 3x4 + 3x3 - 11x2 - 5x + 10 is completely divisible by 3x2 - 5, find all its zeroes.
Solution
Since, 3x2 - 5 divides f(x) completely
 (3x2 - 5) is a factor of f(x)
3 (x2 -
(3x2 - 5) is a factor of f(x)
3 (x2 - 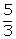 ) is a factor of f(x)
) is a factor of f(x)

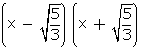 is a factor of f(x)
is a factor of f(x)

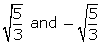 are zeroes of f(x)
are zeroes of f(x)

 (x2 + x - 2) is a factor of f(x)
(x2 + x - 2) is a factor of f(x)
 (x2 + 2x - x - 2) is a factor of f(x)
(x2 + 2x - x - 2) is a factor of f(x)
 (x + 2) (x - 1) is a factor of f(x)
(x + 2) (x - 1) is a factor of f(x)
 -2 and 1 are zeroes of f(x)
Thus, all the zeroes of f(x) are
-2 and 1 are zeroes of f(x)
Thus, all the zeroes of f(x) are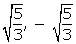 , -2 and 1.
, -2 and 1.
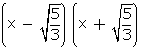 is a factor of f(x)
is a factor of f(x)

Q14. The sum and the product of the zeroes of a quadratic polynomial are 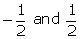 respectively, then the polynomial is:
respectively, then the polynomial is:
Solution

Q15. The number of zeroes for the polynomial y = p (x) from the given graph is:
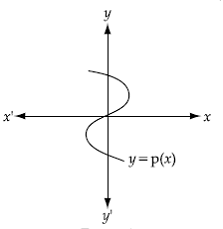

Solution
The number of zeroes of the polynomial y=p(x) from the given graph=number of points at which the graph intersects x axis.
Since the graph intersects the x-axis at only one point, the number of zeroes of the polynomial is one.
Q16. Check
whether x2 + 3x + 1 is a factor of 3x4 + 5x3
- 7x2 + 2x + 2.
Solution
 Remainder
= 0
Thus,
x2 + 3x + 1 is a factor of 3x4 + 5x3 - 7x2
+ 2x + 2.
Remainder
= 0
Thus,
x2 + 3x + 1 is a factor of 3x4 + 5x3 - 7x2
+ 2x + 2.
Q17. If the squared difference of the zeros of the quadratic polynomial f (x) = x2 + px + 45 is equal to 144, find the value of p.
Solution
Let the zeros of quadratic polynomial f (x) = x2 + px + 45 be α and β
α + β = -p
αβ = 45
(α - β)2 = 144
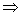 (α - β)2 - 4αβ = 144
(α - β)2 - 4αβ = 144
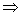 p2 - 4
p2 - 4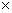 45 = 144
45 = 144
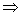 p2 = 144 + 180 = 324
p2 = 144 + 180 = 324
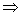 p2 = 324 or p =
p2 = 324 or p =  Hence p =
Hence p = 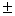 18
18
 Hence p =
Hence p =
Q18. Sum and the product of zeroes of the polynomial x2 +7x +10 is
Solution

Q19. The number of polynomials having zeroes -2 and 5 is:
Solution
The polynomials having -2 and 5 as the zeroes can be written in the form
k(x + 2) (x - 5), where k is a constant.
Thus, number of polynomials with roots -2 and 5 are infinitely many, since k can take infinitely many values.
Q20. What must be added to f(x) = 2x4 + 6x3 - 4x + 8, so that the resulting polynomial is divisible by g(x) = x2 - x + 1.
Solution
By the division algorithm,
f(x) = g(x) q(x) + r(x)f(x) + [−r(x)] = g(x) q(x) + r(x)
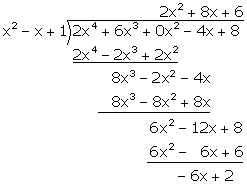 Remainder r(x) = −6x + 2Adding -r(x) = 6x - 2 to f(x) gives the polynomial which is divisible by g(x).
Remainder r(x) = −6x + 2Adding -r(x) = 6x - 2 to f(x) gives the polynomial which is divisible by g(x).
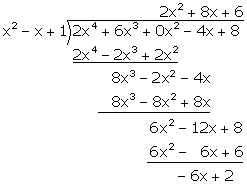 Remainder r(x) = −6x + 2Adding -r(x) = 6x - 2 to f(x) gives the polynomial which is divisible by g(x).
Remainder r(x) = −6x + 2Adding -r(x) = 6x - 2 to f(x) gives the polynomial which is divisible by g(x).
Q21. If α and β are the roots of the polynomial f (x) = x2 - 2x + 3, find a polynomial whose roots are α + 2, β + 2.
Solution
Since α and β are the roots of the polynomial f (x) = x2 - 2x + 3
α + β = 2
αβ = 3
Let S and P be the sum and product of the zeros of the required polynomial. Then,
S = α + 2 + β + 2 = α + β + 4 = 2 + 4 = 6
P = (α + 2)(β + 2)+ 4 = αβ + 2(α + β) = 3 + 2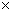 2 + 4 = 11
Hence the required polynomial g(x) is given by
g (x) = k(x2 - Sx + P)
g (x) = k(x2 - 6x + 11), where k is any nonzero real number.
2 + 4 = 11
Hence the required polynomial g(x) is given by
g (x) = k(x2 - Sx + P)
g (x) = k(x2 - 6x + 11), where k is any nonzero real number.
Q22. Obtain all the zeros of the polynomial f(x) = 2x4 + x3 - 14x2 - 19x - 6, if two of its zeros are -2 and -1.
Solution

Q23. Check
whether x2 - x + 1 is a factor of x3 - 3x2 +
3x - 2
Solution
 Quotient
= x - 2, Remainder = 0
Thus,
x2 - x + 1 is a factor of x3 - 3x2 + 3x - 2.
Quotient
= x - 2, Remainder = 0
Thus,
x2 - x + 1 is a factor of x3 - 3x2 + 3x - 2.
Q24. If the sum of the zeros of quadratic polynomial f (x) = kt2 + 2t + 3k is equal to their product, find the value of k.
Solution
Let the zeros of quadratic polynomial f (x) = kt2 + 2t + 3k be α and β


Q25. On
dividing the polynomial p(x) = 9x4 - 4x2 + 4 by the
polynomial g(x) = 3x2 + x - 1, the remainder is ax - b. Find a and
b.
Solution
 Remainder
= -x + 4
Comparing
this with ax - b, we get,
a
= -1
b
= -4
Remainder
= -x + 4
Comparing
this with ax - b, we get,
a
= -1
b
= -4
Q26. If α, β, γ are zeroes of polynomial 6x3 + 3x2 - 5x + 1, then find the value of α-1 + β-1 + γ-1
Solution
Given p(x) = 6x3 + 3x2 - 5x + 1
a = 6, b = 3, c = -5, d = 1
α, β and γ are zeroes of p(x).










Q27. Verify that -2 and -5 are the zeros of the polynomial x2 + 7x + 10.
Solution
A real number k is said to be a zero of polynomial p(x), if p (k) = 0
p (-2) = (-2)2 + 7 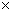 (-2) + 10
= 4 – 14 + 10
p (-2) = 0
p (-5) = (-5)2 + 7
(-2) + 10
= 4 – 14 + 10
p (-2) = 0
p (-5) = (-5)2 + 7 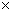 (-5) + 10
= 25 – 35 + 10
p (-5) = 0
Hence -2 and -5 are the zeros of the given polynomial.
(-5) + 10
= 25 – 35 + 10
p (-5) = 0
Hence -2 and -5 are the zeros of the given polynomial.
Q28. Find the quotient and remainder when x5
+3x4 - 5x3 + 14x2 + 39x - 11 is divided by
4x + x2 - 2.
Solution
Rearranging the terms of divisor
in descending order of degree, we get
 Clearly, the degree of remainder
9x + 5 is less than the degree of divisor.
x2 + 4x - 2.
∴ Quotient, q(x) = x3
- x2 + x + 8 and remainder, r(x) = 9x + 5.
Clearly, the degree of remainder
9x + 5 is less than the degree of divisor.
x2 + 4x - 2.
∴ Quotient, q(x) = x3
- x2 + x + 8 and remainder, r(x) = 9x + 5.
 Clearly, the degree of remainder
9x + 5 is less than the degree of divisor.
x2 + 4x - 2.
∴ Quotient, q(x) = x3
- x2 + x + 8 and remainder, r(x) = 9x + 5.
Clearly, the degree of remainder
9x + 5 is less than the degree of divisor.
x2 + 4x - 2.
∴ Quotient, q(x) = x3
- x2 + x + 8 and remainder, r(x) = 9x + 5.
Q29. Using the division algorithm, find the divisor if the quotient is p - 3, the remainder is p - 4 and the dividend is p2 + 3p - 7.
Solution
f(x) = p2 + 3p - 7, g(x) = ?, r(x) = p - 4 and q(x) = p - 3
f(x) = q(x) g(x) + r(x)
p2 + 3p - 7 = (p - 3)g(x) + p - 4
∴ (p - 3)g(x) = p2 + 3p - 7 - p + 4
∴ (p - 3)g(x) = p2 + 2p - 3
∴ g(x) = 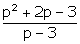 ∴ g(x) =
∴ g(x) = 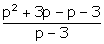 ∴ g(x) =
∴ g(x) = 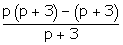 ∴ g(x) =
∴ g(x) = 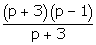 ∴ g(x) = p - 1
∴ g(x) = p - 1
Q30. On dividing 3x3 - 2x2 + 5x - 5 by a polynomial p(x), the quotient and the remainder are x2 - x + 2 and -7 respectively. Find p(x).
Solution

Q31. If two of the zeroes of the polynomial p(x) = 5x4 - 5x3 - 33x2 + 3x + 18 are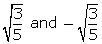 , find the other two zeroes.
, find the other two zeroes.
Solution
Since 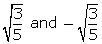 are zeroes of p(x)
are zeroes of p(x)
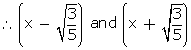 are factors of p(x)
are factors of p(x)
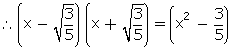 is a factor of p(x)
Or, (5x2 - 3) is a factor of p(x)
is a factor of p(x)
Or, (5x2 - 3) is a factor of p(x)

 p(x) = (5x2 - 3) (x2 - x - 6)
=
p(x) = (5x2 - 3) (x2 - x - 6)
= 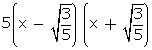 (x - 3) (x + 2)
(x - 3) (x + 2)
 Other zeroes of p(x) are 3 and -2.
Other zeroes of p(x) are 3 and -2.
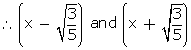 are factors of p(x)
are factors of p(x)
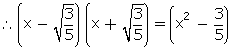 is a factor of p(x)
Or, (5x2 - 3) is a factor of p(x)
is a factor of p(x)
Or, (5x2 - 3) is a factor of p(x)

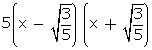 (x - 3) (x + 2)
(x - 3) (x + 2)
Q32. If the remainder on division of x3
+ 2x2 + kx + 3 by x - 3 is 21, then find the quotient and value of
k. Hence, find the zeroes of the cubic polynomial x3 + 2x2
+ kx - 18.
Solution
We have the following terms:
Dividend: f(x) = x3 +
2x2 + kx + 3,
Divisor: g(x) = x - 3 and
remainder, r (x) = 21
Using the remainder thermo, we
have the following expression:
f(3) = 21
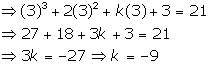 The polynomial p(x) is x3
+ 2x2 - 9x + 3.
Now, on long division, we get
The polynomial p(x) is x3
+ 2x2 - 9x + 3.
Now, on long division, we get
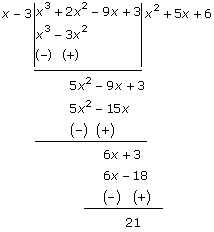 Thus, x3 + 2x2
- 9x + 3 = (x - 3 ) (x2 + 5x + 6) + 21
∴ The quotient = x2
+ 5x + 6
Clearly, x3
+ 2x2 - 9x - 18
= (x - 3 )
(x2 + 5x + 6)
= (x - 3 )
(x + 2)(x + 3)
Therefore,
the zeroes of x3 + 2x2 - 9x -
18 are 3, -2 and -3.
Thus, x3 + 2x2
- 9x + 3 = (x - 3 ) (x2 + 5x + 6) + 21
∴ The quotient = x2
+ 5x + 6
Clearly, x3
+ 2x2 - 9x - 18
= (x - 3 )
(x2 + 5x + 6)
= (x - 3 )
(x + 2)(x + 3)
Therefore,
the zeroes of x3 + 2x2 - 9x -
18 are 3, -2 and -3.
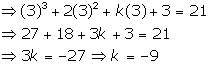 The polynomial p(x) is x3
+ 2x2 - 9x + 3.
Now, on long division, we get
The polynomial p(x) is x3
+ 2x2 - 9x + 3.
Now, on long division, we get
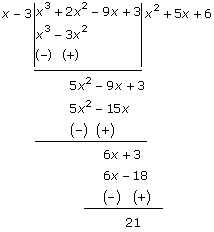 Thus, x3 + 2x2
- 9x + 3 = (x - 3 ) (x2 + 5x + 6) + 21
∴ The quotient = x2
+ 5x + 6
Clearly, x3
+ 2x2 - 9x - 18
= (x - 3 )
(x2 + 5x + 6)
= (x - 3 )
(x + 2)(x + 3)
Therefore,
the zeroes of x3 + 2x2 - 9x -
18 are 3, -2 and -3.
Thus, x3 + 2x2
- 9x + 3 = (x - 3 ) (x2 + 5x + 6) + 21
∴ The quotient = x2
+ 5x + 6
Clearly, x3
+ 2x2 - 9x - 18
= (x - 3 )
(x2 + 5x + 6)
= (x - 3 )
(x + 2)(x + 3)
Therefore,
the zeroes of x3 + 2x2 - 9x -
18 are 3, -2 and -3.
Q33. If one solution of the equation 3x2 = 8x + 2k + 1 is seven times the other. Find the solutions and the value of k.
Solution
3x2 = 8x + 2k + 1
3x2 - 8x - 2k - 1 = 0
Let α is one zero.
Then, β = 7α is the other zero
α + 7α = 8/3
8α = 8/3
α = 1/3
β = 7/3


Q34. Find
all other zeroes of the polynomial p (x) = 2x3 + 3x2 -
11x - 6, if one of its zero is -3.
Solution
p
(x) = 2x3 + 3x2 - 11x - 6
One
zero is -3. So, (x + 3) is a factor of p (x).
 Quotient = 2x2 - 3x - 2 = (2x + 1)
(x - 2)
Thus, the other zeroes of p(x) are 2 and
Quotient = 2x2 - 3x - 2 = (2x + 1)
(x - 2)
Thus, the other zeroes of p(x) are 2 and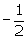 .
Hence, all zeroes of p (x) is -3, 2 and
.
Hence, all zeroes of p (x) is -3, 2 and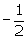 .
.
 Quotient = 2x2 - 3x - 2 = (2x + 1)
(x - 2)
Thus, the other zeroes of p(x) are 2 and
Quotient = 2x2 - 3x - 2 = (2x + 1)
(x - 2)
Thus, the other zeroes of p(x) are 2 and
Q35. Divide
(6 + 23x + 25x2 + 6x3) by (3 + 7x + 2x2) and
verify the division algorithm.
Solution
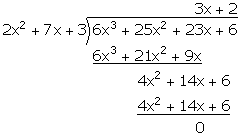 Quotient
= 2 + 3x
Remainder
= 0
Verification:
It
can be seen that:
(3
+ 7x + 2x2) (2 + 3x) + 0 = 6 + 23x + 25x2 + 6x3
Quotient
= 2 + 3x
Remainder
= 0
Verification:
It
can be seen that:
(3
+ 7x + 2x2) (2 + 3x) + 0 = 6 + 23x + 25x2 + 6x3
Q36. On
dividing 3x3 - 2x2 + 5x - 5 by a polynomial p(x), the
quotient and remainder are x2 - x + 2 and -7 respectively. Find
p(x).
Solution
By division algorithm,
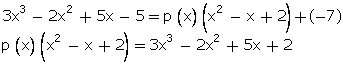

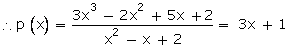
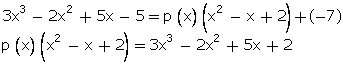

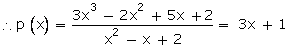
Q37. Find all zeroes of polynomial 4x4 - 20x3 + 23x2 + 5x - 6 if two of its zeroes are 2 and 3.
Solution
Given 2 and 3 are the zeroes of the polynomial.
Thus(x - 2) (x - 3) are factors of this polynomial
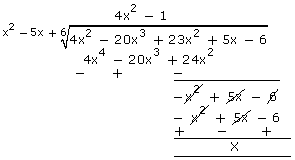 4x4 - 20x3 + 23x2 + 5x - 6 = (x2 - 5x + 6) (4x2 - 1)
Thus, 4x4 - 20x3 + 23x2 +5x-6=(x - 2) (x - 3) (2x - 1) (2x + 1)
Hence, 2, 3,
4x4 - 20x3 + 23x2 + 5x - 6 = (x2 - 5x + 6) (4x2 - 1)
Thus, 4x4 - 20x3 + 23x2 +5x-6=(x - 2) (x - 3) (2x - 1) (2x + 1)
Hence, 2, 3, 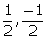 are the zeroes of the given polynomial.
are the zeroes of the given polynomial.
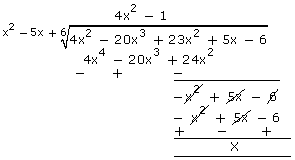 4x4 - 20x3 + 23x2 + 5x - 6 = (x2 - 5x + 6) (4x2 - 1)
Thus, 4x4 - 20x3 + 23x2 +5x-6=(x - 2) (x - 3) (2x - 1) (2x + 1)
Hence, 2, 3,
4x4 - 20x3 + 23x2 + 5x - 6 = (x2 - 5x + 6) (4x2 - 1)
Thus, 4x4 - 20x3 + 23x2 +5x-6=(x - 2) (x - 3) (2x - 1) (2x + 1)
Hence, 2, 3,
Q38. Divide x4 - 3x2 +
4x + 5 by x2 - x + 1 and verify that
Dividend = Divisor 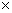 Quotient +
Reminder.
Quotient +
Reminder.
Solution
Arranging the terms in descending order,
we get
 Clearly, the degree of remainder 8 is
zero, which is less than the degree of x2 - x + 1.
Clearly, the degree of remainder 8 is
zero, which is less than the degree of x2 - x + 1.
 Quotient = x2 + x - 3 and remainder = 8.
Verification:
Divisor
Quotient = x2 + x - 3 and remainder = 8.
Verification:
Divisor 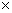 Quotient +
Reminder = (x2 - x + 1) (x2 + x - 3) + 8
= x4 + x3 - 3x2
- x3 - x2 + 3x + x2 + x - 3 + 8
= x4 + x3- x3
- 3x2 - x2 + x2 + 3x + x -3 +8
= x4 - 3x2 +
4x + 5 = dividend
Quotient +
Reminder = (x2 - x + 1) (x2 + x - 3) + 8
= x4 + x3 - 3x2
- x3 - x2 + 3x + x2 + x - 3 + 8
= x4 + x3- x3
- 3x2 - x2 + x2 + 3x + x -3 +8
= x4 - 3x2 +
4x + 5 = dividend
 Clearly, the degree of remainder 8 is
zero, which is less than the degree of x2 - x + 1.
Clearly, the degree of remainder 8 is
zero, which is less than the degree of x2 - x + 1.
Q39. Find the zeroes of  x2 + 5x -
x2 + 5x -  and verify the relation between the zeroes and coefficients of the polynomial.
and verify the relation between the zeroes and coefficients of the polynomial.
 x2 + 5x -
x2 + 5x -  and verify the relation between the zeroes and coefficients of the polynomial.
and verify the relation between the zeroes and coefficients of the polynomial.Solution
 Hence, the relation between the zeroes and coefficients of the polynomial is verified.
Hence, the relation between the zeroes and coefficients of the polynomial is verified.
Q40. Divide
x4 - 3x2 + 4x + 5 by x2 - x + 1, find
quotient and remainder.
Solution
 Quotient
= x2 + x - 3
Remainder
= 8
Quotient
= x2 + x - 3
Remainder
= 8
Q41. If 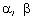 are the zeroes of f(x) = px2 - 2x + 3p and
are the zeroes of f(x) = px2 - 2x + 3p and 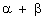 =
= 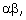 then the value of p is:
then the value of p is:
Solution

Q42. If α and β are the roots of the polynomial f (x) = 6x2 + x - 2, find the value of 

Solution
Since α and β are the roots of the polynomial f (x) = 6x2 + x - 2






Q43. Find the quotient and reminder using division algorithm:
f(x) = 15x3 - 20x2 + 13x - 12, g(x) = 2 - 2x + x2
Solution
We have the following equations:
f(x) = 15x3 - 20x2 + 13x - 12 and
g(x) = 2 - 2x + x2 is x2 - 2x + 2
Clearly, degree of f(x) = 3 and degree of g(x) = 2. Therefore, the degree of quotient q(x) = 3 - 2 = 1 and degree of remainder r(x) is less than the degree of g(x), i.e. 2.
Let quotient, q(x) = ax + b and remainder, r(x) = cx + d.
Using division algorithm, we have the following equation:
p(x) = g(x) × q(x) + r(x)
∴15x3 - 20x2 + 13x - 12
= (x2 - 2x + 2) (ax + b) + (cx + d)
= ax3 + bx2 - 2ax2 - 2bx + 2ax + 2b + cx + d
= ax3 + (b - 2a)x2 + (2a + c - 2b) x + (2b + d)
Comparing the coefficient of same powers of x on both sides, we get
a = 15 [Comparing the coefficient of x3]
b - 2a = -20 [Comparing the coefficient of x2]
2a + c - 2b = 13 [Comparing the coefficient of x]
2b + d = -12 [Comparing the constant terms ]
Solving the above equation, we get the following values:
a = 15, b = 10, c = 3 and d = -32
Hence, quotient, q(x) = 15x + 10 and remainder, r(x) = 3x - 32.
Q44. It is being given that 1 is one of the zeros of the polynomial 7x - x3 - 6. Find its other zeros.
Solution
It is given that 1 is a zero of the polynomial -x3 + 7x - 6. So, (x - 1) is a factor of -x3 + 7x - 6.
Now, we have:
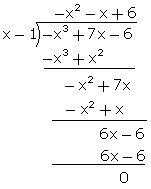 (-x3 + 7x - 6)
(-x3 + 7x - 6) 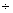 (x - 1) = (-x2 - x + 6)
- (x2 + x - 6) = -(x + 3) (x - 2)
(x - 1) = (-x2 - x + 6)
- (x2 + x - 6) = -(x + 3) (x - 2)
 Other zeros are -3 and 2.
Other zeros are -3 and 2.
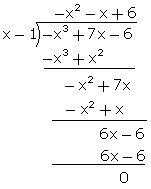 (-x3 + 7x - 6)
(-x3 + 7x - 6)
Q45. Find the zeroes of the polynomial 100x2 - 81.
Solution
Since a2 - b2 = (a + b)(a - b)
100x2 - 81 = (10x + 9)(10x - 9)
Thus, the required zeroes are  and
and 
 and
and 
Q46. Which of the following functions are not polynomials. Give reason for your answer. i)  (ii) x2 + x + 3
(iii)
(ii) x2 + x + 3
(iii)  (iv)
(iv)
 (ii) x2 + x + 3
(iii)
(ii) x2 + x + 3
(iii)  (iv)
(iv)
Solution
In (i) the powers of x are 3, -2, -1, and 0. Since -2, -1 are not non-negative integers, therefore it is not a polynomial.
In (ii) the powers of x are 2, 1, 0. Since 2, 1 and 0 are positive integers, therefore it is a polynomial.
In (iii) the powers of the variable u are  , 1, and 0. Since
, 1, and 0. Since  is not non-negative integer, therefore it is not a polynomial.
In (iv) the powers of x are 3, 0, 1 and 0. As 3, 0, 1, 0 are positive integers, therefore it is a polynomial.
is not non-negative integer, therefore it is not a polynomial.
In (iv) the powers of x are 3, 0, 1 and 0. As 3, 0, 1, 0 are positive integers, therefore it is a polynomial.
 , 1, and 0. Since
, 1, and 0. Since  is not non-negative integer, therefore it is not a polynomial.
In (iv) the powers of x are 3, 0, 1 and 0. As 3, 0, 1, 0 are positive integers, therefore it is a polynomial.
is not non-negative integer, therefore it is not a polynomial.
In (iv) the powers of x are 3, 0, 1 and 0. As 3, 0, 1, 0 are positive integers, therefore it is a polynomial.
Q47. What must be subtracted from the polynomial 8x4 + 14x3 + x2 + 7x + 8 so that the resulting polynomial is exactly divisible by 4x2 - 3x + 2?
Solution
 Thus, when 6x + 2 is subtracted from the given polynomial 8x4 + 14x3 + x2 + 7x + 8, then it will be divisible by 4x2 - 3x + 2.
Thus, when 6x + 2 is subtracted from the given polynomial 8x4 + 14x3 + x2 + 7x + 8, then it will be divisible by 4x2 - 3x + 2.
Q48. Find
all the zeroes of p(x) = x3 - 9x2 - 12x + 20, if (x +
2) is a factor of p(x).
Solution
Given,
x + 2 is a factor of p(x).
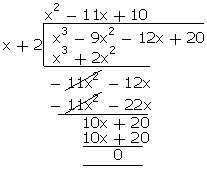
 p(x) = (x + 2) (x2 - 11x + 10)
= (x + 2) (x2 - 10x -
x + 10)
= (x + 2) (x (x - 10) - (x - 10))
= (x + 2) (x - 1) (x - 10)
p(x) = (x + 2) (x2 - 11x + 10)
= (x + 2) (x2 - 10x -
x + 10)
= (x + 2) (x (x - 10) - (x - 10))
= (x + 2) (x - 1) (x - 10)
 Zeroes of p(x) are -2, 1, 10.
Zeroes of p(x) are -2, 1, 10.
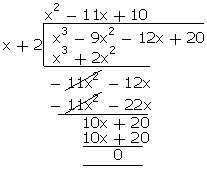
Q49. If (x + a) is a factor of two polynomials x2 + px + q and x2 + mx + n, then prove that: 

Solution
(x + a) is a factor of x2 + px + q
 (-a)2 + p(-a) + q = 0
(-a)2 + p(-a) + q = 0
 a2 - ap + q = 0.
a2 = ap - q ..(i)
(x + a) is a factor of x2 + mx + n
a2 - ap + q = 0.
a2 = ap - q ..(i)
(x + a) is a factor of x2 + mx + n
 (-a)2 + m (-a) + n = 0
(-a)2 + m (-a) + n = 0
 a2 - am + n = 0
a2= am - n ...(ii)
From (i) and (ii),
ap - q = am - n
ap - am = q - n
a(p - m) = q - n
a =
a2 - am + n = 0
a2= am - n ...(ii)
From (i) and (ii),
ap - q = am - n
ap - am = q - n
a(p - m) = q - n
a = 

Q50. What must be added to x3 - 4x2 + x - 6 so that x2 + 2x - 3 becomes its factor?
Solution
(x3 - 4x2 + x - 6) (x2 + 2x - 3)
(x2 + 2x - 3)
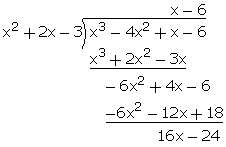 Remainder = 16x - 24
Thus, the required expression that must be added is
Remainder = 16x - 24
Thus, the required expression that must be added is  16x - 24
16x - 24
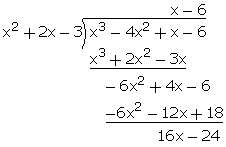 Remainder = 16x - 24
Thus, the required expression that must be added is
Remainder = 16x - 24
Thus, the required expression that must be added is  16x - 24
16x - 24
Q51. If α, β are the zeros of the polynomial 25p2 - 15p + 2, find a quadratic polynomial whose zeros are  and
and 
 and
and 
Solution
α and β are two roots of 25p2 - 15p + 2
 αβ =
αβ =  For the required polynomial,
Sum of the zeros =
For the required polynomial,
Sum of the zeros =  Product of zeroes =
Product of zeroes =


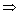 a = 8, b = -30, c = 25
Therefore, required polynomial is 8x2 - 30x + 25.
a = 8, b = -30, c = 25
Therefore, required polynomial is 8x2 - 30x + 25.
 αβ =
αβ =  For the required polynomial,
Sum of the zeros =
For the required polynomial,
Sum of the zeros =  Product of zeroes =
Product of zeroes =


Q52. The graph of the polynomial p(x) intersects the x-axis three times in distinct points, then which of the following could be an expression for p(x):
Solution
Since, the graph of the polynomial p(x) intersects the x-axis at three distinct points, it will have 3 distinct roots.
Hence, it will be a cubic polynomial.
Thus, amongst the given alternatives the polynomial p(x) can be 4 - 4x - x2 + x3.
Q53. If a and b are the zeroes of the polynomial x2 - 5x + k such that a - b = 1, find the value of k.
Solution
x2 - 5x + k
 .....(i)
.....(i)
 α - β = 1 ...(ii)
Solving (i) and (ii) we get α = 3 and β = 2
Hence, k = αβ = 3 × 2 = 6
α - β = 1 ...(ii)
Solving (i) and (ii) we get α = 3 and β = 2
Hence, k = αβ = 3 × 2 = 6
 .....(i)
.....(i)
 α - β = 1 ...(ii)
Solving (i) and (ii) we get α = 3 and β = 2
Hence, k = αβ = 3 × 2 = 6
α - β = 1 ...(ii)
Solving (i) and (ii) we get α = 3 and β = 2
Hence, k = αβ = 3 × 2 = 6
Q54. On
dividing the polynomial 4x4 - 5x3 - 39x2 -
46x - 2 by the polynomial g(x) the quotient and remainder are x2 -
3x - 5 and -5x + 8 respectively. Find g(x).
Solution
p(x)
= 4x4 - 5x3 - 39x2 - 46x - 2
q(x)
= x2 - 3x - 5
r(x)
= -5x + 8
g(x)
= 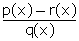 =
= 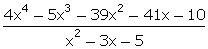
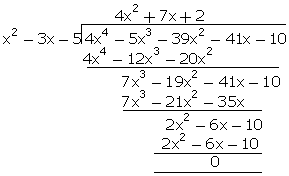 g(x)
= 4x2 + 7x + 2
g(x)
= 4x2 + 7x + 2
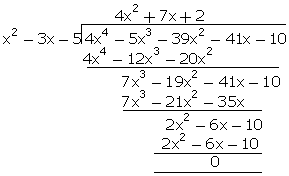 g(x)
= 4x2 + 7x + 2
g(x)
= 4x2 + 7x + 2
Q55. On
dividing the polynomial p(x) = 5x4 - 4x3 + 3x2
- 2x + 1 another polynomial g(x) = x2 + 2, if the quotient is ax2
+ bx + c, find a, b and c.
Solution
 Comparing
the quotient obtained with ax2 + bx + c, we get,
a
= 5
b
= -4
c
= -7
Comparing
the quotient obtained with ax2 + bx + c, we get,
a
= 5
b
= -4
c
= -7
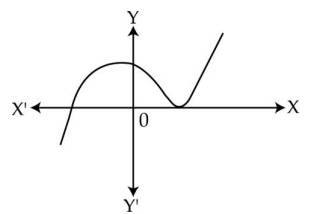
Q56. The graph of y = p(x) is given below. The number of zeroes of p(x) are :

Solution
The number of zeroes of a polynomial p(x) is the number of times its graph intersects or touches the x-axis.
The given graph touches the x-axis twice, so the number of zeroes of the polynomial y = p(x) is 2.
Q57. Obtain all the zeroes of the polynomial f(x) = x4 - 7x3 + 10x2 + 14x - 24, if two of its zeroes are +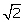 and
and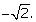
Solution
Since,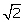 and
and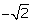 are zeroes of f(x).
are zeroes of f(x).
 (x -
(x - 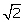 ) and (x +
) and (x + 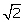 ) are factors of f(x)
) are factors of f(x)
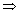 (x -
(x - 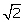 ) (x +
) (x + 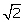 ) is a factor is f(x)
) is a factor is f(x)
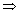 (x2 - 2) is factor of f(x)
We have,
(x2 - 2) is factor of f(x)
We have,

 (x2 - 7x + 12) is a factor of f(x)
(x2 - 7x + 12) is a factor of f(x)
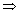 (x - 3) (x - 4) is a factor of f(x)
(x - 3) (x - 4) is a factor of f(x)
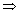 (x - 3) and (x - 4) are factors of f(x)
(x - 3) and (x - 4) are factors of f(x)
 x = 3 and x = 4 are other zeroes of f(x)
Hence, all the zeroes of f(x) are
x = 3 and x = 4 are other zeroes of f(x)
Hence, all the zeroes of f(x) are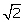 , -
, -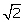 3 and 4.
3 and 4.

Q58. If the polynomial x4 - 6x3 + 16x2 - 25x + 10 is divided by another polynomial x2 - 2x + k, the remainder comes out to be x + a, find the values of k and a.
Solution
If the polynomial x4 - 6x3 + 16x2 - 25x + 10 on division by x2 - 2x + k leaves remainder (x + a).
Then, polynomial (x4 - 6x3 + 16x2 - 25x + 10) - (x + a) on division by x2 - 2x + k leaves remainder zero.
On long division of polynomial
(x4 - 6x3 + 16x2 - 25x + 10) - (x + a) = x4 - 6x3 + 16x2 - 26x + 10 -a by x2 - 2x + k, the remainder obtained is (-10 + 2k ) x + ( 10 - a - 8k + k2).
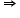 (-10 + 2k )x + ( 10 - a - 8k + k2) = 0
(-10 + 2k )x + ( 10 - a - 8k + k2) = 0
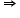 -10 + 2k = 0 and 10 - a - 8k + k2 = 0
-10 + 2k = 0 and 10 - a - 8k + k2 = 0
 k = 5 and a = -5
k = 5 and a = -5
 (-10 + 2k )x + ( 10 - a - 8k + k2) = 0
(-10 + 2k )x + ( 10 - a - 8k + k2) = 0
 -10 + 2k = 0 and 10 - a - 8k + k2 = 0
-10 + 2k = 0 and 10 - a - 8k + k2 = 0
 k = 5 and a = -5
k = 5 and a = -5
Q59. Find the zeroes of the polynomial 

Solution
 The zeros are
The zeros are 
Q60. Find the zeroes of the polynomial x2 + 3x - 10 and verify the relation between its zeroes and coefficient.
Solution
We have p(x) = x2 + 3x - 10 = (x + 5)(x - 2)
For any zero, p(x) = 0
 x2 + 3x - 10 = 0
x2 + 3x - 10 = 0
 (x + 5)(x - 2) = 0
(x + 5)(x - 2) = 0
 (x + 5) = 0 OR (x - 2) = 0
(x + 5) = 0 OR (x - 2) = 0
 x = - 5 OR x = 2
The zeros of p(x) = x2 + 3x - 10 are as α = -5 and β = 2
Now, sum of zeros = α + β = -5 + 2 = -3 =
x = - 5 OR x = 2
The zeros of p(x) = x2 + 3x - 10 are as α = -5 and β = 2
Now, sum of zeros = α + β = -5 + 2 = -3 =  Product of zeros = αβ = (-5) × 2 = - 10 =
Product of zeros = αβ = (-5) × 2 = - 10 = 
 x2 + 3x - 10 = 0
x2 + 3x - 10 = 0
 (x + 5)(x - 2) = 0
(x + 5)(x - 2) = 0
 (x + 5) = 0 OR (x - 2) = 0
(x + 5) = 0 OR (x - 2) = 0
 x = - 5 OR x = 2
The zeros of p(x) = x2 + 3x - 10 are as α = -5 and β = 2
Now, sum of zeros = α + β = -5 + 2 = -3 =
x = - 5 OR x = 2
The zeros of p(x) = x2 + 3x - 10 are as α = -5 and β = 2
Now, sum of zeros = α + β = -5 + 2 = -3 =  Product of zeros = αβ = (-5) × 2 = - 10 =
Product of zeros = αβ = (-5) × 2 = - 10 = 
Q61. Find the quotient and reminder using division algorithm:
f(x) = 10x4 + 17x3 - 62x2 + 30x - 3, g(x)=2x2 + 7x + 1
Solution
We have the following equations:
f(x) = 10x4 + 17x3 - 62x2 + 30x - 3 and g(x) = 2x2 + 7x + 1.
Clearly, degree of f(x) = 4 and degree of g(x) = 2. Therefore, degree of quotient, q(x) = 4 - 2 = 2 and degree of remainder, r(x) is less than degree of g(x), i.e. 2.
Let quotient, q(x) = ax2 + bx + c and remainder, r(x) = dx + e
Using division algorithm, we have the following equation:
f(x) = g(x) × q(x) + r(x)
∴10x4 + 17x3 - 62x2 + 30x - 3
= (2x2 + 7x + 1) (ax2 + bx + c) + (dx + e)
= 2ax4 + 2bx3 + 2cx2 + 7ax3 + 7bx2 + 7cx + ax2 + bx + c + dx + e
= 2ax4 + (7a + 2b)x3 + (a + 7b + 2c)x2 + (b + 7c + d)x + (c + e)
Comparing the coefficient of same powers of x on both sides, we get
2a = 10 [Comparing the power of x4]
7a + 2b = 17 [Comparing the power of x3]
a + 7b + 2c = -62 [comparing the power of x2]
b + 7c + d = 30 [comparing the power of x]
c + e = -3 [comparing the constant terms]
Solving the above equations, we get the following values:
a = 5, b = -9, c = -2, d = 53 and e = -1
Hence, quotient, q (x) = 5x2 - 9x - 4 and remainder,
r(x) = 53x - 1.
Q62. Find the number of zeros in the following graphs. 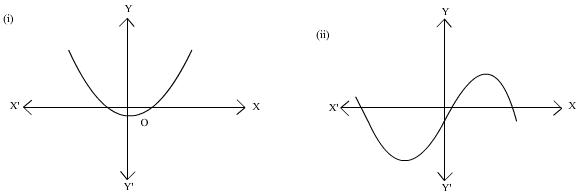

Solution
In (i) the graph intersects the x-axis at two points, hence there are two zeros.
In (ii) the graph intersects the x-axis at three points, hence there are three zeros.
Q63. Find the value of k for which the polynomial x4 + 10x3 + 25x 2 + 15 x + k is exactly divisible by x + 7
Solution

Q64. Find the polynomial of least degree which
should be subtracted from the polynomial 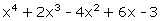 so that it is
exactly divisible by x2 - x + 1.
so that it is
exactly divisible by x2 - x + 1.
Solution
Here, p(x) = x4
+ 2x3 - 4x2 + 6x - 3, g(x) = x2 - x +1
On dividing p(x) by
g(x)
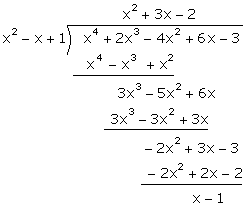 Therefore (x-1) must be
subtracted from the polynomial p(x) to make it divisible by g(x).
Therefore (x-1) must be
subtracted from the polynomial p(x) to make it divisible by g(x).
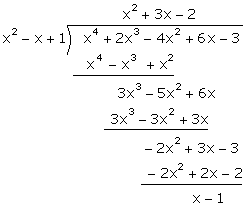 Therefore (x-1) must be
subtracted from the polynomial p(x) to make it divisible by g(x).
Therefore (x-1) must be
subtracted from the polynomial p(x) to make it divisible by g(x).
Q65. 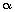 and
and 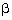 are zeroes of the quadratic polynomial x2 - 6x + a. Find the value of 'a' if 3
are zeroes of the quadratic polynomial x2 - 6x + a. Find the value of 'a' if 3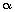 + 2
+ 2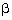 = 20.
= 20.
Solution
p(x) = x2 - 6x + a
 ...(1)
Given, 3α + 2β = 20... (2)
Multiplying (1) by 3,
3α + 3β = 18 .....(3)
On solving (2) and (3), we get:
β = -2, α = 8
Now, αβ = a
...(1)
Given, 3α + 2β = 20... (2)
Multiplying (1) by 3,
3α + 3β = 18 .....(3)
On solving (2) and (3), we get:
β = -2, α = 8
Now, αβ = a
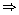 (8)
(8) 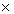 (-2) = a
(-2) = a
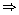 a = -16
a = -16
 ...(1)
Given, 3α + 2β = 20... (2)
Multiplying (1) by 3,
3α + 3β = 18 .....(3)
On solving (2) and (3), we get:
β = -2, α = 8
Now, αβ = a
...(1)
Given, 3α + 2β = 20... (2)
Multiplying (1) by 3,
3α + 3β = 18 .....(3)
On solving (2) and (3), we get:
β = -2, α = 8
Now, αβ = a
Q66. On
dividing the polynomial p(x) by polynomial g(x) = 4x2 + 3x - 2,
the quotient is q(x) = 2x2 + 2x - 1 and remainder is r(x) = 14x -
10. Find the polynomial p(x).
Solution
p(x)
= q(x) 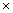 g(x) + r(x)
(By division algorithm)
= (2x2 + 2x - 1) (4x2
+ 3x - 2) + 14x - 10
= 8x4
+ 6x3 - 4x2 + 8x3 + 6x2 - 4x - 4x2
- 3x + 2 + 14x - 10
= 8x4 + 14x3 - 2x2
+ 7x - 8
g(x) + r(x)
(By division algorithm)
= (2x2 + 2x - 1) (4x2
+ 3x - 2) + 14x - 10
= 8x4
+ 6x3 - 4x2 + 8x3 + 6x2 - 4x - 4x2
- 3x + 2 + 14x - 10
= 8x4 + 14x3 - 2x2
+ 7x - 8
Q67. Sum of the two zeroes of a polynomial of degree 4 is -1 and their product is -2. If other two zeroes are 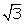 and -
and -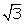 . Find the polynomial.
. Find the polynomial.
Solution
Two zeroes of polynomial p(x) and 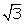 and -
and -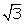
 (x -
(x - 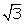 ) and (x +
) and (x + 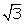 ) are factors of p(x)
) are factors of p(x)
 (x -
(x - 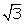 ) (x +
) (x + 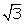 ) is a factor of p(x)
) is a factor of p(x)
 x2 - 3 is a factor of p(x)
Since, degree of p(x) is 4, so the other factor of p(x) will also be a quadratic polynomial.
Now, it is also given that the sum of the other two zeroes of p(x) is -1 and their product is -2.
So, the other factor is
x2 - (sum of roots) x + product of roots
i.e., x2 + x - 2
x2 - 3 is a factor of p(x)
Since, degree of p(x) is 4, so the other factor of p(x) will also be a quadratic polynomial.
Now, it is also given that the sum of the other two zeroes of p(x) is -1 and their product is -2.
So, the other factor is
x2 - (sum of roots) x + product of roots
i.e., x2 + x - 2
 p(x) = (x2 - 3) (x2 + x - 2) = x4 + x3 - 5x2 - 3x + 6
p(x) = (x2 - 3) (x2 + x - 2) = x4 + x3 - 5x2 - 3x + 6
Q68. Divide the
polynomial p(x) = 3x2 - x3 - 3x + 5 by g(x) = x - 1 - x2
and find its quotient and remainder.
Solution
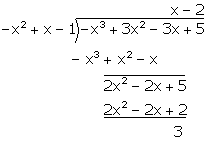 Quotient = x - 2, Reminder = 3
Quotient = x - 2, Reminder = 3
Q69. Divide (2x2 + x - 20) by (x + 3) and verify the result by division algorithm.
Solution
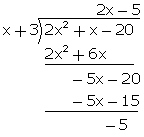 Quotient = 2x - 5, remainder = -5
Verification:
It can be seen that:
(x + 3) (2x - 5) - 5 = 2x2 + 6x - 5x - 15 - 5 = 2x2 + x - 20
Quotient = 2x - 5, remainder = -5
Verification:
It can be seen that:
(x + 3) (2x - 5) - 5 = 2x2 + 6x - 5x - 15 - 5 = 2x2 + x - 20
Q70. On
dividing the polynomial p(x) = 5x4 -4x3 + 3x2
- 2x + 1 by another polynomial g(x) = x2 + 2, if the quotient is
ax2 + bx + c, find a, b and c.
Solution
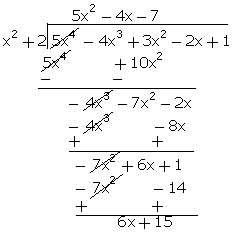 Comparing
with the obtained quotient with ax2 + bx + c, we get,
a = 5
b = -4
c = -7
Comparing
with the obtained quotient with ax2 + bx + c, we get,
a = 5
b = -4
c = -7
Q71. By applying the division algorithm prove that the polynomial g(x) = x2 + 3x + 1 is a factor of the polynomial f(x) = 3x4 + 5x3 - 7x2 + 2x + 2.
Solution

Q72. Find the quotient and reminder using division algorithm:
f(x) = x3 - 6x2 + 11x - 6, g(x) = x + 1
Solution
We have:
f(x) = x3 - 6x2 + 11x - 6 and g(x) = x + 1
Clearly, degree of f(x) = 3 and degree of g(x) = 1. Therefore, the degree of quotient is q(x) = 3 - 1 = 2 and the degree of remainder is r(x) = 0
Let quotient q(x) = ax2 + bx + c and remainder r(x) = k.
Using division algorithm, we have
f(x) = g(x) × q(x) + r(x)
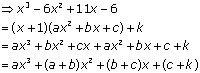 Comparing the coefficient of same powers of x on both sides, we get
a = 1 [Comparing the coefficient of x3]
a + b = -6 [Comparing the coefficient of x2]
b + c = 11 [Comparing the coefficient of x]
c + k = -6 [Comparing the constant terms ]
Solving the above equations, we get the following values:
a = 1, b = -7, c = 18, and k = -24
∴ Quotient is q (x) = x2 - 7x + 18 and remainder is r(x) = -24.
Comparing the coefficient of same powers of x on both sides, we get
a = 1 [Comparing the coefficient of x3]
a + b = -6 [Comparing the coefficient of x2]
b + c = 11 [Comparing the coefficient of x]
c + k = -6 [Comparing the constant terms ]
Solving the above equations, we get the following values:
a = 1, b = -7, c = 18, and k = -24
∴ Quotient is q (x) = x2 - 7x + 18 and remainder is r(x) = -24.
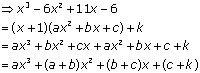 Comparing the coefficient of same powers of x on both sides, we get
a = 1 [Comparing the coefficient of x3]
a + b = -6 [Comparing the coefficient of x2]
b + c = 11 [Comparing the coefficient of x]
c + k = -6 [Comparing the constant terms ]
Solving the above equations, we get the following values:
a = 1, b = -7, c = 18, and k = -24
∴ Quotient is q (x) = x2 - 7x + 18 and remainder is r(x) = -24.
Comparing the coefficient of same powers of x on both sides, we get
a = 1 [Comparing the coefficient of x3]
a + b = -6 [Comparing the coefficient of x2]
b + c = 11 [Comparing the coefficient of x]
c + k = -6 [Comparing the constant terms ]
Solving the above equations, we get the following values:
a = 1, b = -7, c = 18, and k = -24
∴ Quotient is q (x) = x2 - 7x + 18 and remainder is r(x) = -24.
Q73. Find the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial 6x2 - 3 - 7x, and verify the relationship between the zeroes and the coefficients.
Solution
6x2 - 7x - 3
= 6x2 - 9x + 2x - 3
= 3x(2x - 3) + (2x - 3)
= (3x + 1)(2x - 3)
Therefore, the two zeroes are  and
and
 Hence, the relationship between the zeroes and the coefficients is verified.
Hence, the relationship between the zeroes and the coefficients is verified.
 and
and
 Hence, the relationship between the zeroes and the coefficients is verified.
Hence, the relationship between the zeroes and the coefficients is verified.
Q74. Find
the values of a and b so that the polynomial p(x) = x4 + x3
+ 8x2 - ax + b is exactly divisible by x2 - 1.
Solution
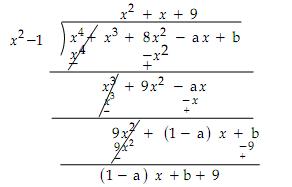 Since,
remainder has to be zero, we have:
1 - a = 0
Since,
remainder has to be zero, we have:
1 - a = 0 

Comments
Post a Comment